Abstract
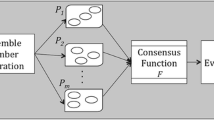
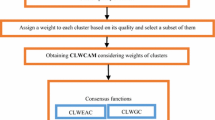
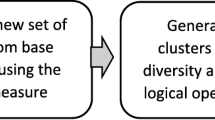
It is well recognized that clustering algorithms play an important role in data analysis. For a successful application of these algorithms, it is crucial to determine the relevant features in the original dataset. To deal with this problem there are efficient techniques for feature selection in the literature. Moreover, it is also well known that, in the clustering task, it is also difficult to define an adequate number of clusters. This paper proposes a new ensemble clustering method that is comprised of three stages: the first generates the clustering ensemble, the second combines the results of the multiple clustering scenarios generated, and the last one creates a new partition using the combined data. To generate the clustering ensemble, the method combines feature selection strategies and clustering with various numbers of clusters to produce a similarity matrix. This similarity matrix is then used to compute the final clustering output. Experiments performed using seven well known datasets showed the effectiveness of the proposed technique.
Supported by CAPES and CNPq.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R Core Team: R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria (2015). https://www.R-project.org/
Armanfard, N., Reilly, J.P., Komeili, M.: Local feature selection for data classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(6), 1217–1227 (2016)
Bolón-Canedo, V., Sánchez-Maroño, N., Alonso-Betanzos, A.: A review of feature selection methods on synthetic data. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 34(3), 483–519 (2013)
Cai, D., Zhang, C., He, X.: Unsupervised feature selection for multi-cluster data. In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 333–342. ACM (2010)
Chandrashekar, G., Sahin, F.: A survey on feature selection methods. Comput. Electr. Eng. 40(1), 16–28 (2014)
Dempster, A.P., Laird, N.M., Rubin, D.B.: Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodological) 39(1), 1–38 (1977)
Dhir, C.S., Lee, J., Lee, S.Y.: Extraction of independent discriminant features for data with asymmetric distribution. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 30(2), 359–375 (2012)
Doak, J.: An evaluation of feature selection methods and their application to computer security. University of California, Computer Science (1992)
Farahat, A.K., Ghodsi, A., Kamel, M.S.: Efficient greedy feature selection for unsupervised learning. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 35(2), 285–310 (2013)
Fern, X.Z., Brodley, C.E.: Random projection for high dimensional data clustering: a cluster ensemble approach. ICML 3, 186–193 (2003)
Fred, A.L., Jain, A.K.: Combining multiple clusterings using evidence accumulation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27(6), 835–850 (2005)
Fukunaga, K.: Introduction to Statistical Pattern Recognition, 2nd edn. Academic Press Professional Inc., San Diego (1990)
Guyon, I., Elisseeff, A.: An introduction to variable and feature selection. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 3, 1157–1182 (2003)
Huang, D., Lai, J.H., Wang, C.D.: Combining multiple clusterings via crowd agreement estimation and multi-granularity link analysis. Neurocomputing 170, 240–250 (2015)
Kolaczyk, E.D., Csárdi, G.: Statistical Analysis of Network Data with R. Springer, New York (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0983-4
Li, N., Latecki, L.J.: Clustering aggregation as maximum-weight independent set. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 782–790 (2012)
Lichman, M.: UCI machine learning repository (2013). http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml
Melnykov, V., Chen, W.C., Maitra, R.: MixSim: an R package for simulating data to study performance of clustering algorithms. J. Stat. Softw. 51(12), 1–25 (2012)
Mendes-Moreira, J., Soares, C., Jorge, A.M., Sousa, J.F.D.: Ensemble approaches for regression: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 45(1), 10 (2012)
Murty, M.N., Devi, V.S.: Pattern Recognition: An Algorithmic Approach. Springer, London (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-85729-495-1
Peter, T.J., Somasundaram, K.: Study and development of novel feature selection framework for heart disease prediction. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2(10), 1–7 (2012)
Strehl, A., Ghosh, J.: Cluster ensembles-a knowledge reuse framework for combining multiple partitions. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 3, 583–617 (2002)
Topchy, A.P., Jain, A.K., Punch, W.F.: A mixture model for clustering ensembles. In: SDM, pp. 379–390. SIAM (2004)
Vega-Pons, S., Ruiz-Shulcloper, J.: A survey of clustering ensemble algorithms. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 25(03), 337–372 (2011)
Wang, X., Yang, C., Zhou, J.: Clustering aggregation by probability accumulation. Pattern Recognit. 42(5), 668–675 (2009)
Yi, J., Yang, T., Jin, R., Jain, A.K., Mahdavi, M.: Robust ensemble clustering by matrix completion. In: IEEE 12th International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 1176–1181. IEEE (2012)
Zhang, C., Ma, Y.: Ensemble Machine Learning. Springer, New York (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9326-7
Zhao, Z., Liu, H.: Spectral feature selection for supervised and unsupervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1151–1157. ACM (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fiol-Gonzalez, S., Almeida, C., Barbosa, S., Lopes, H. (2018). A Novel Committee–Based Clustering Method. In: Ordonez, C., Bellatreche, L. (eds) Big Data Analytics and Knowledge Discovery. DaWaK 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11031. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98539-8_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98539-8_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-98538-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-98539-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)