Abstract
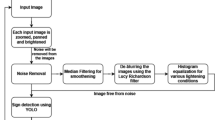
Safer autonomous navigation might be challenging if there is a failure in sensing system. Robust classifier algorithm irrespective of camera position, view angles, and environmental condition of an autonomous vehicle including different size & type (Car, Bus, Truck, etc.) can safely regulate the vehicle control. As training data play a crucial role in robust classification of traffic signs, an effective augmentation technique enriching the model capacity to withstand variations in urban environment is required. In this paper, a framework to identify model weakness and targeted augmentation methodology is presented. Based on off-line behavior identification, exact limitation of a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model is estimated to augment only those challenge levels necessary for improved classifier robustness. Predictive Augmentation (PA) and Predictive Multiple Augmentation (PMA) methods are proposed to adapt the model based on acquired challenges with a high numerical value of confidence. We validated our framework on two different training datasets and with 5 generated test groups containing varying levels of challenge (simple to extreme). The results show impressive improvement by \(\approx \) 5–20% in overall classification accuracy thereby keeping their high confidence.
Supported by Systems Safety Architecture (EPXS), Scania CV AB, Södertälje, Sweden.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Autonomous-vehicle technology is advancing ever faster, The Economist - Special report. https://www.economist.com/special-report/2018/03/01/autonomous-vehicle-technology-is-advancing-ever-faster. Accessed 1 Mar 2018
Nowakowski, C., Shladover, S.E., Tan, H.S.: Heavy vehicle automation: human factors lessons learned. Procedia Manuf. 3, 2945–2952 (2015)
44 Corporations Working On Autonomous Vehicles, Autotech (CB Insights). https://www.cbinsights.com/research/autonomous-driverless-vehicles-corporations-list/. Accessed 18 May 2017
Heineke, K., Kampshoff, P., Mkrtchyan, A., Shao, E.: Self-driving car technology: when will the robots hit the road? Mckinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/automotive-and-assembly/our-insights/self-driving-car-technology-when-will-the-robots-hit-the-road. Accessed May 2017
Nguwi, Y.Y., Kouzani, A.Z.: Detection and classification of road signs in natural environments. Neural Comput. Appl. 17(3), 265–289 (2008)
Lafuente-Arroyo, S., Gil-Jimenez, P., Maldonado-Bascon, R., Lopez-Ferreras, F., Maldonado-Bascon, S.: Traffic sign shape classification evaluation I: SVM using distance to borders. In: IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, pp. 557–562 (2005)
Mathias, M., Timofte, R., Benenson, R., Van Gool, L.: Traffic sign recognition - how far are we from the solution?. In: IEEE International Joint conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8 (2013)
CireşAn, D., Meier, U., Masci, J., Schmidhuber, J.: Multi-column deep neural network for traffic sign classification. Neural Netw. 32, 333–338 (2012)
Stallkamp, J., Schlipsing, M., Salmen, J., Igel, C.: The German traffic sign recognition benchmark: a multi-class classification competition. In: IEEE International Joint conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1453–1460 (2011)
Timofte, R., Zimmermann, K., Van Gool, L.: Multi-view traffic sign detection, recognition, and 3D localisation. Mach. Vis. Appl. 25(3), 633–647 (2014)
Temel, D., Kwon, G., Prabhushankar, M., AlRegib, G.: CURE-TSR: Challenging Unreal and Real Environments for Traffic Sign Recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.02463 (2017)
Sermanet, P., LeCun, Y.: Traffic sign recognition with multi-scale convolutional networks. In: IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 2809–2813 (2011)
Bansal, A., Badino, H., Huber, D.: Understanding how camera configuration and environmental conditions affect appearance-based localization. In: Intelligent Vehicles Symposium Proceedings, pp. 800–807 (2014)
Zhang, C., Bengio, S., Hardt, M., Recht, B., Vinyals, O.: Understanding deep learning requires rethinking generalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.03530 (2016)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Zeng, Y., Xu, X., Shen, D., Fang, Y., Xiao, Z.: Traffic sign recognition using kernel extreme learning machines with deep perceptual features. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 18(6), 1647–1653 (2017)
Jin, J., Fu, K., Zhang, C.: Traffic sign recognition with hinge loss trained convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 15(5), 1991–2000 (2014)
Gonzalez, R.C., Woods, R.E.: Digital Image Processing, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River (2012)
Joshi, P.: OpenCV with Python By Example. Packt Publishing Ltd, Birmingham (2015)
Mordvintsev, A., Abid, K.: Opencv-python tutorials documentation. https://media.readthedocs.org/pdf/opencv-python-tutroals/latest/opencv-python-tutroals.pdf. Accessed 5 Nov 2017
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Nazre Batool, Christopher Norén for Heavy vehicle data, Sribalaji CA, Ashokan Arumugam, and Abhishek S for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Harisubramanyabalaji, S.P., ur Réhman, S., Nyberg, M., Gustavsson, J. (2018). Improving Image Classification Robustness Using Predictive Data Augmentation. In: Gallina, B., Skavhaug, A., Schoitsch, E., Bitsch, F. (eds) Computer Safety, Reliability, and Security. SAFECOMP 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11094. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99229-7_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99229-7_49
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-99228-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-99229-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)