Abstract
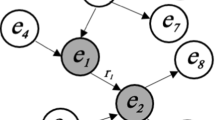
Knowledge graphs are networks with annotated nodes and edges, representing different relations between the network nodes. Learning from such graphs is becoming increasingly important as numerous real-life systems can be represented as knowledge graphs, where properties of selected types of nodes or edges are learned. This paper presents a fully autonomous approach to targeted knowledge graph decomposition, advancing the state-of-the-art HINMINE network decomposition methodology. In this methodology, weighted edges between the nodes of a selected node type are constructed via different typed triplets, each connecting two nodes of the same type through an intermediary node of a different type. The final product of such a decomposition is a weighted homogeneous network of the selected node type. HINMINE is advanced by reformulating the supervised network decomposition problem as a combinatorial optimization problem, and by solving it by a differential evolution approach. The proposed approach is tested on node classification tasks on two real-life knowledge graphs. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed end-to-end learning approach is much faster and as accurate as the exhaustive search approach.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The machine used for evaluation was an of-the-shelf Lenovo y510p laptop with an i7 Intel processor (8 cores) and 4 GB of RAM.
- 2.
The feature matrix is not memory efficient, as it uses \(\mathcal {O}(N^{2})\) space, yet optimization of this part of the procedure is out of the scope of this study.
References
Burt, R., Minor, M.: Applied Network Analysis: A Methodological Introduction. Sage Publications, Beverly Hills (1983)
Sun, Y., Han, J.: Mining Heterogeneous Information Networks: Principles and Methodologies. Morgan & Claypool Publishers, San Rafael (2012)
Consortium: Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene ontology consortium. Nat. Genet. 25(1), 25–29 (2000)
Ehrlinger, L., Wöß, W.: Towards a definition of knowledge graphs. In: SEMANTiCS (Posters, Demos, SuCCESS) (2016)
Nickel, M., Murphy, K., Tresp, V., Gabrilovich, E.: A review of relational machine learning for knowledge graphs. Proc. IEEE 104(1), 11–33 (2016)
Kralj, J., Robnik-Šikonja, M., Lavrač, N.: HINMINE: heterogeneous information network mining with information retrieval heuristics. J. Intell. Inf. Syst., 1–33 (2017)
Sen, P., Namata, G., Bilgic, M., Getoor, L., Galligher, B., Eliassi-Rad, T.: Collective classification in network data. AI Mag. 29(3), 93 (2008)
de Sousa, C.A.R., Rezende, S.O., Batista, G.E.A.P.A.: Influence of graph construction on semi-supervised learning. In: Blockeel, H., Kersting, K., Nijssen, S., Železný, F. (eds.) ECML PKDD 2013. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 8190, pp. 160–175. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40994-3_11
Perozzi, B., Al-Rfou, R., Skiena, S.: Deepwalk: Online learning of social representations. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 701–710. ACM (2014)
Wang, Q., Mao, Z., Wang, B., Guo, L.: Knowledge graph embedding: a survey of approaches and applications. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 29(12), 2724–2743 (2017)
Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Feng, J., Chen, Z.: Knowledge graph embedding by translating on hyperplanes. In: Proceedings of AAAI, vol. 14, pp. 1112–1119 (2014)
Cai, H., Zheng, V.W., Chang, K.: A comprehensive survey of graph embedding: problems, techniques and applications. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. (2018)
Wang, D., Cui, P., Zhu, W.: Structural deep network embedding. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 1225–1234. ACM (2016)
Tang, J., Qu, M., Wang, M., Zhang, M., Yan, J., Mei, Q.: Line: Large-scale information network embedding. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web, International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee, pp. 1067–1077 (2015)
Grčar, M., Trdin, N., Lavrač, N.: A methodology for mining document-enriched heterogeneous information networks. Comput. J. 56(3), 321–335 (2013)
Kralj, J., Valmarska, A., Robnik-Šikonja, M., Lavrač, N.: Mining text enriched heterogeneous citation networks. In: Cao, T., et al. (eds.) PAKDD 2015. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 9077, pp. 672–683. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-18038-0_52
Žitnik, M., Leskovec, J.: Predicting multicellular function through multi-layer tissue networks. Bioinformatics 33(14), i190–i198 (2017)
Fleetwood, K.: An introduction to differential evolution. In: Proceedings of Mathematics and Statistics of Complex Systems (MASCOS) One Day Symposium, 26th November, Brisbane, Australia, pp. 785–791 (2004)
Price, K., Storn, R.M., Lampinen, J.A.: Differential Evolution: A Practical Approach to Global Optimization. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-31306-0
Das, S., Mullick, S.S., Suganthan, P.N.: Recent advances in differential evolution-an updated survey. Swarm Evol. Comput. 27, 1–30 (2016)
Das, S., Suganthan, P.N.: Differential evolution: a survey of the state-of-the-art. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 15(1), 4–31 (2011)
Jones, E., Oliphant, T., Peterson, P.: SciPy: Open Source Scientific Tools for Python (2014)
Škrlj, B., Kralj, J., Vavpetič, A., Lavrač, N.: Community-based semantic subgroup discovery. In: Appice, A., Loglisci, C., Manco, G., Masciari, E., Ras, Z.W. (eds.) NFMCP 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10785, pp. 182–196. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78680-3_13
Orchard, S., et al.: The MIntAct project-IntAct as a common curation platform for 11 molecular interaction databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(Database issue), pp. D358–D363 (2014)
Marchler-Bauer, A., et al.: CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(D1), D222–D226 (2014)
Szklarczyk, D., et al.: String v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(D1), D447–D452 (2014)
Kelley, L.A., Mezulis, S., Yates, C.M., Wass, M.N., Sternberg, M.J.: The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 10(6), 845 (2015)
Finn, R.D., et al.: Interpro in 2017beyond protein family and domain annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 45(D1), D190–D199 (2016)
Lee, J., Konc, J., Janežič, D., Brooks, B.R.: Global organization of a binding site network gives insight into evolution and structure-function relationships of proteins. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 11652 (2017)
Škrlj, B., Kunej, T., Konc, J.: Insights from ion binding site network analysis into evolution and functions of proteins. Mol. Inform. (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Škrlj, B., Kralj, J., Lavrač, N. (2018). Targeted End-to-End Knowledge Graph Decomposition. In: Riguzzi, F., Bellodi, E., Zese, R. (eds) Inductive Logic Programming. ILP 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11105. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99960-9_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99960-9_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-99959-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-99960-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)