Abstract
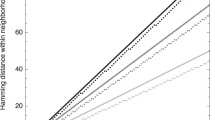
An effect of the loss of diversity and the rapid concentration of an initially broadly spread population is analyzed for models of phenotypic evolution. The impact of the population size, different selection schemes, and dimensionality of the search space on population diversity is studied. Obtained results confirm common opinions that in large populations the diversity is greater and that the stronger selection pressure causes the faster concentration. High dimensional search spaces do not restrain the concentration of a population. In this case, populations cluster even faster than in one-dimensional search space.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blickle, T., Thiele, L.: A comparison of selection schemes used in evolutionary algorithms. Evolutionary Computation 4(4), 361–395 (1996)
Chora̧życzewski, A., Galar, R., Karcz-Dulȩba, I.: Considering phenotypic Evolution in the Space of Population States. In: Rutkowski, L., Tadeusiewicz, R. (eds.) Proc. 5th Conf. on Neural Networks and Soft Computing, Zakopane, pp. 615–620 (2000)
Chora̧życzewski, A., Galar, R.: Evolutionary Dynamics of Population States. In: Proc. Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Seoul, Korea, pp. 1366–1373 (2001)
Galar, R.: Handicapped individua in evolutionary processes. Biol. Cyberern. 51(1), 1–9 (1985)
Karcz-Dulȩba, I.: Dynamics of evolution of population of two in the space of population states. The case of symmetrical fitness functions. In: Proc. 4th Nat. Conf. on Evol. Algorithms and Global Opt., La̧dek Zdrój, Poland, pp. 115–122 (2000) (in Polish)
Karcz-Dulȩba, I.: Evolution of Two-element Population in the Space of Population States: Equilibrium States for Asymmetrical Fitness Functions. In: Arabas, J. (ed.) Evolutionary Algorithms and Global Optimization, Warsaw, pp. 35–46. Univ. of Technology Press (2002)
Karcz-Dulȩba, I.: Analysis of population concentration in phenotypic evolution. In: Workshop on Evolutionary Computation, Wdzydze (2003) (in Polish)
Michalewicz, Z.: Genetic Algorithms +Data Structures=Evolution Programs. Springer, Heidelberg (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Karcz-Dulȩba, I. (2004). Concentration of Population in Phenotypic Evolution. In: Rutkowski, L., Siekmann, J.H., Tadeusiewicz, R., Zadeh, L.A. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing - ICAISC 2004. ICAISC 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3070. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24844-6_61
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24844-6_61
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-22123-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-24844-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive