Abstract
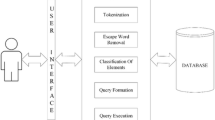
This paper addresses the problem of mapping Natural Language to SQL queries. It assumes that the input is in English language and details a methodology to build a SQL query based on the input sentence, a dictionary and a set of production rules. The dictionary consists of semantic sets and index files. A semantic set is created for each table or attribute name and contains synonyms, hyponyms and hypernyms as retrieved by WordNet and complemented manually. The index files contain pointers to records in the database, ordered by value and by data type. The dictionary and the production rules form a context-free grammar for producing the SQL queries. The context ambiguities are addressed through the use of the derivationally related forms based on WordNet. Building the run time semantic sets of the input tokens helps solving the ambiguities related to the database schema. The proposed method introduces two functional entities: a pre-processor and a runtime engine. The pre-processor reads the database schema and uses WordNet to create the semantic sets and the set of production rules. It also reads the database records and creates the index files. The run time engine matches the input tokens to the dictionary and uses the rules to create the corresponding SQL query.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller, G.: WordNet: A Lexical Database for English. Communications of the ACM 38(1), 39–41 (1995)
Stratica, N., Kosseim, L., Desai, B.C.: NLIDB Templates for Semantic Parsing. In: Proceedings of Applications of Natural Language to Data Bases, NLDB 2003, Burg, Germany, June 2003, pp. 235–241 (2003)
Minker, J.: Information storage and retrieval - a survey and functional description. In: SIGIR, vol. 12, pp. 1–108 (1997)
Rubin, S.H., Chen, S.-C., Shyu, M.-L.: Field-Effect Natural Language Semantic Mapping. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man & Cybernetics, Washington, D.C., USA, October 5-8, pp. 2483–2487 (2003)
Mazlack, L.J., Feinauer, R.A.: Establishing a Basis for Mapping Natural- Language Statements Onto a Database Query Language. In: SIGIR, pp. 192–202 (1980)
Allen, J.: Natural Language Understanding, University of Rochester, The Benjamin Cummings Publishing Company, Inc. (1995) ISBN: 0-8053-0334-0
Baker, K., Franz, A., Jordan, P.: Coping with Ambiguity in Knowledge- based Natural Language Analysis. In: Florida AI Research Symposium, Pensacola, Florida, pp. 155–159 (1994)
Hirst, G.: Semantic Interpretation and the Resolution of Ambiguity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1986)
Latent Semantic Analysis Laboratory at the Colorado University site visited in (March 2004), http://lsa.colorado.edu/
Sleator, D., Temperley, D.D.: Parsing English with A Link Grammar .In:Proceedings of the Third Annual Workshop on Parsing Technologies (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Stratica, N., Desai, B.C. (2004). Schema-Based Natural Language Semantic Mapping. In: Meziane, F., Métais, E. (eds) Natural Language Processing and Information Systems. NLDB 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3136. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-27779-8_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-27779-8_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-22564-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-27779-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive