Abstract
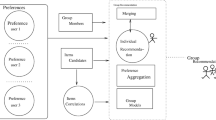
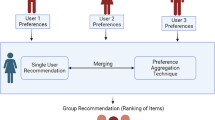
In recent years, recommender systems have achieved great success. Popular sites give thousands of recommendations every day. However, despite the fact that many activities are carried out in groups, like going to the theater with friends, these systems are focused on recommending items for sole users. This brings out the need of systems capable of performing recommendations for groups of people, a domain that has received little attention in the literature. In this article we introduce a novel method of making collaborative recommendations for groups, based on models built using techniques from symbolic data analysis. After, we empirically evaluate the proposed method to see its behaviour for groups of different sizes and degrees of homogeneity, and compare the achieved results with both an aggregation-based methodology previously proposed and a baseline methodology.
The authors would like to thank CNPq and CAPES (Brazilian Agencies) for their financial support.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herlocker, J., Konstan, J., Borchers, A., Riedl, J.: An algorithm framework for performing collaborative filtering. In: Proc. of the 22nd ACM SIGIR Conference, Berkley, pp. 230–237 (1999)
Hill, W., Stead, L., Rosenstein, M., Furnas, G.: Recommending and evaluating choices in a virtual community of use. In: Proc. of the ACM CHI 1995 Conference, Denver, pp. 194–201 (1995)
Lieberman, H., Van Dyke, N., Vivacqua, A.: Let’s browse: A collaborative web browsing agent. In: Proc. of the IUI 1999, L.A., pp. 65–68 (1999)
O’Connor, M., Cosley, D., Konstan, J., Riedl, J.: Polylens: A recommender system for groups of users. In: Proc. of the 7th ECSCW Conference, Bonn, pp. 199–218 (2001)
Arrow, K.J.: Social Choice and Individual Values. Wiley, New York (1963)
Hinsz, V.: Group decision making with responses of a quantitative nature: The theory of social schemes for quantities. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 80, 28–49 (1999)
Bock, H., Diday, E.: Analysis of Symbolic Data: Exploratory Methods for Extracting Statistical Information from Complex Data. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Queiroz, S., De Carvalho, F., Ramalho, G., Corruble, V.: Making recommendations for groups using collaborative filtering and fuzzy majority. In: Bittencourt, G., Ramalho, G.L. (eds.) SBIA 2002. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2507, pp. 248–258. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Chiclana, F., Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., Poyatos, M.: A classification method of alternatives for multiple preference ordering criteria based on fuzzy majority. Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics 4, 801–813 (1996)
Kendall, M.: Rank Correlation Methods, 4th edn. Charles Griffin & Company, London (1975)
Dwork, C., Kumar, R., Moni, N., Sivakumar, D.: Rank aggregation methods for the web. In: Proc. of the WWW10 Conference, Hong Kong, pp. 613–622 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
de M. Queiroz, S.R., de A.T. de Carvalho, F. (2004). Making Collaborative Group Recommendations Based on Modal Symbolic Data. In: Bazzan, A.L.C., Labidi, S. (eds) Advances in Artificial Intelligence – SBIA 2004. SBIA 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3171. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28645-5_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28645-5_31
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-23237-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-28645-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive