Abstract
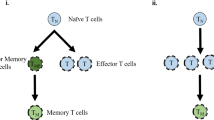
As an empirical knowledge on vaccination, it is known that immune memories against viral antigens (i.e., self-reproductive antigens) are sustained for a very long period more than 10 years, whereas against non-viral antigens, they are sustained only for a relatively short period less than a few years. This fact suggests that an immune system switches adaptability its memory strategy according to degree of antigen’s self-reproductive rate, its hazard rate. Therefore it is an interesting knowledge though, so far, a theory that indicates a causal relationship between durability of an immune memory and an antigen’s viral/non-viral character has not been clarified.
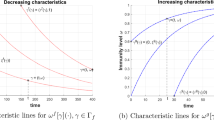
This study demonstrates why the durability of an immune memory depends on the viral/non-viral antigen character by taking a dynamical approach. Concretely, when an antigen increases its self-reproductive rate, the system changes at a critical self-reproductive rate, its memory strategy from a “forgettable” immune memory embedded in a transient dynamics to an “unforgettable” one done in a dynamical attractor.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roitt, I., Brostoff, J., Male, D.: Immunology, 5th edn. Mosby International Ltd., London (1998)
Jerne, N.K.: Ann. Immunol. 125C, 373–389 (1974)
Richiter, P.H.: Eur. J. Immunol. 5, 350–354 (1975)
Hoffmann, G.W.: Regulation of Immune Response Dynamics. In: De Lisi, C., Hiernaux, J.R.J. (eds.), vol. 1, pp. 137–162 (1982)
De Boer, R.J., Hogeweg, P.: Bull. Math. Biol. 51(2), 223–246 (1989)
De Boer, R.J.: In Theoretical Immunology Parts II, pp. 265–289. Addison-Wesley Pub. Company Inc., New York (1988)
Harada, K., Ikegami, T., Shiratori, N.: Proc. of Seventh International Conference on Knowledge-based Intelligent Information Engineering Systems, pp. 519–523. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Harada, K. (2004). A Switching Memory Strategy in an Immune Network Model. In: Negoita, M.G., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L.C. (eds) Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems. KES 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3214. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30133-2_68
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30133-2_68
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-23206-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-30133-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive