Abstract
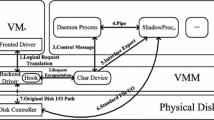
Logical Volume Manager (LVM) has been a key subsystem for online disk storage management. Additional layer is created in the kernel to present a logical view of physical storage devices. Many transparent functions can be implemented between the logical and physical layers, such as merging several physical disks into a larger logical device, resizing logical devices without stopping the system. In a logical volume group, files can be striped into several physical disks so as to achieve high I/O performance. But data I/O parallelism by itself does not guarantee the optimal performance of an application since higher data throughput does not necessarily result in better application performance. This paper studied the dynamic load balancing and data redistribution algorithms in the storage virtualization layer when the load becomes imbalanced across the disks due to access pattern fluctuation. An extension of the heuristic load balancing method was proposed to the storage virtualization subsystem of Tsinghua-Mass Storage Network System (TH-MSNS). Logical volume I/O request status is monitored and the physical disks are sorted according to the access number of Logical Extents (LE) per time unit. The I/O operations on a LE of the hottest disk are transparently migrated to other disks. The preliminary performance simulations under a WWW server file access workload give satisfactory results by the promising cooling algorithm in storage virtualization systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilson, S.: Managing a Fibre Channel Storage Area Net work. Storage Networking Industry Association (November 1998)
Kim, M.Y.: Synchronized Disk Interleaving. IEEE trans. On computers C-35(11) (1986)
Salem, K., Garcia-Molina, H.: Disk Striping. In: Proc. Of the 2nd Int. Conf. On Data Engineering (1986)
Weikum, G., Zabback, P., Scheuermann, P.: Dynamic File Allocation in Disk Arrays. In: ACM SIGMOD Conf. (1991)
Tsai, H.P., Huang, J.L., Chao, C.M., et al.: SIFA: A Scalable File System with Intelligent File Allocation. In: Proc. of the 26th Int. COMPSAC (2002)
Scheuermann, P., Weikum, G., Zabback, P.: Data Partitioning and Load Balancing in Parallel Disk Systems. VLDB J. 7(1), 48–66 (1998)
Awerbuch, B., Bartal, Y., Fiat, A.: Competitive Distributed File Allocation. Information and Computation 185, 1–40 (2003)
Ahmad, I., Karlapalem, K., Kwok, Y.K., et al.: Evolutionary Algorithms for Allocating Data in Distributed Database Systems. Distributed and Parallel Databases 11, 5–32 (2002)
Shu, J.W., et al.: A Highly Efficient FC-SAN Based on Load Stream. In: Zhou, X., Xu, M., Jähnichen, S., Cao, J. (eds.) APPT 2003. LNCS, vol. 2834, pp. 31–40. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Schwetman, H.: CSIM19: A Powerful Tool for Building System Models. In: Peters, B.A., Smith, J.S., Medeiros, D.J., Roher, M.W. (eds.) Proceedings of the 2001 Winter Simulation Conference, Washington, D.C., pp. 250–255 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sun, W., Shu, Jw., Zheng, W. (2004). Storage Virtualization System with Load Balancing for SAN. In: Jin, H., Pan, Y., Xiao, N., Sun, J. (eds) Grid and Cooperative Computing - GCC 2004 Workshops. GCC 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3252. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30207-0_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30207-0_32
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-23578-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-30207-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive