Abstract
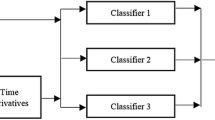
Task classification is an important subproblem of Spoken Language Understanding (SLU) in automated systems providing natural language user interface, whose goal is to identify the topic of a query from the user. This paper presents a combination of multiple statistical classifiers to improve the accuracy of task classification in the context of city public transportation information inquiry domain. Three different typical types of statistical classifiers are trained on the same data to be the base classifiers of the combination system: naïve bayes classifier, n-gram model, and support vector machines. The combination method of two-stage classification is emplored to yield better overall performance. Our experiments showed that support vector machines outperform excessively the other base classifiers for task classification in our domain. The comparative experimental results between two-stage classification and voting strategy indicated, under the circumstance that the best base classifier has the overwhelming performance over the other base classifiers, the strategy of two-stage classification was more effective and could produce better results than the best component classifier.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cettolo, M., Corazza, A., De Mori, R.: A Mixed Approach to Speech Understanding. In: Proc. of ICSLP, Philadelphia, USA (1996)
Wang, Y.-Y., Acero, A., Chelba, C., Frey, B., Wong, L.: Combination of statistical and rule-based approaches for spoken language understanding. In: Proc. of ICSLP, Denver Colorado, USA, September 2002, pp. 609–612 (2002)
Chelba, C., Mahajan, M., Acero, A.: Speech Utterance Classification. In: Proc. of ICASSP, Hong Kong (April 2003)
Lee, C.-H., Carpenter, B., Chou, W., Chu-Carroll, J., Reichl, W., Saad, A., Zhou, Q.: On natural language call routing. Speech Communication 31(4), 309–320 (2000)
Marineau, J., Wiemer-Hastings, P., Harter, D., Olde, B., Chipman, P., Karnavat, A., Pomeroy, V., Graesser, A.C.: TRG: Classification of speech acts in tutorial dialog. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Tutorial Dialogue at the Intelligent Tutoring Systems 2000 Conference, Canada, pp. 57–63 (2000)
Mast, M., Kompe, R., Harbeck, S., Kiessling, A., Niemann, H., Nöth, E., Schukat-Talamazzini, E.G., Warnke, V.: Dialog act classification with the help of prosody. In: Proc. of ICSLP, Philadelphia (1996)
van Halteren, H., Zavrel, J., Daelemans, W.: Improving accuracy in word class tagging through the combination of machine learning systems. Computational Linguistics 27(2), 199–230 (2001)
Larkey, L.S., Croft, W.B.: Combining Classifiers in Text Categorization. In: Proceedings of the 19th Annual International Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR 1996), Zurich, Switzerland, pp. 289–297 (1996)
Wu, W., Lu, R., Liu, Z.: Comparative experiments on task classification for spoken language understanding using naive Bayes classifier. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Knowledge Engineering (IEEE) 2003, Beijing, October 2003, pp. 492–497 (2003)
Ney, H., Essen, U., Kneser, R.: On structuring probabilistic dependen-cies in stochastic language modeling. Computer Speech and Language 8, 1–38 (1994)
Sebastiani, F.: Machine learning in automated text categorization. ACM Computing Surveys 34(1), 1–47 (2002)
Màrquez, L.: Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing, Technical Report LSI-00-45-R, Departament de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Espana (2000)
Mitchell, T.M.: Machine Learning, pp. 52–53. McGraw-Hill, New York (1996)
Quinlan, J.R.: C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo (1996)
Manning, C.D., Schütze, H.: Foundation of Statistical Natural Language Processing, pp. 589–597. The MIT Press, Cambridge (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, WL., Lu, RZ., Gao, F., Yuan, Y. (2005). Combining Multiple Statistical Classifiers to Improve the Accuracy of Task Classification. In: Gelbukh, A. (eds) Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing. CICLing 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3406. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30586-6_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30586-6_50
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-24523-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-30586-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)