Abstract
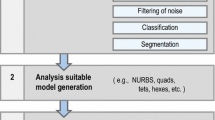
We describe an approach to construct hexahedral solid NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) meshes for patient-specific vascular geometric models from imaging data for use in isogeometric analysis. First, image processing techniques, such as contrast enhancement, filtering, classification, and segmentation, are used to improve the quality of the input imaging data. Then, lumenal surfaces are extracted by isocontouring the preprocessed data, followed by the extraction of vascular skeleton via Voronoi and Delaunay diagrams. Next, the skeleton-based sweeping method is used to construct hexahedral control meshes. Templates are designed for various branching configurations to decompose the geometry into mapped meshable patches. Each patch is then meshed using one-to-one sweeping techniques, and boundary vertices are projected to the lumenal surface. Finally, hexahedral solid NURBS are constructed and used in isogeometric analysis of blood flow. Piecewise linear hexahedral meshes can also be obtained using this approach. Examples of patient-specific arterial models are presented.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. Taylor C.A., Hughes T.J., Zarins C.K. “Finite element modeling of blood flow in arteries.” Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, vol. 158, 155–196, 1998
2. Bazilevs Y., Calo V., Zhang Y., Hughes T.J. “Isogeometric Fluid-Structure Interaction Analysis with Applications to Arterial Blood Flow.” Computational Mechanics, 2006
3. Hughes T.J., Cottrell J.A., Bazilevs Y. “Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry, and mesh refinement.” Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, vol. 194, 4135–4195, 2005
4. Cottrell J., Reali A., Bazilevs Y., Hughes T. “Isogeometric analysis of structural vibrations.” Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2005. In press
5. Bazilevs Y., da Veiga L.B., Cottrell J., Hughes T., Sangalli G. “Isogeometric analysis: Approximation, stability and error estimates for h-refined meshes.” Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences, 2006. Submitted, available as ICES report 06-04
6. Rogers D.F. An Introduction to NURBS With Historical Perspective. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 2001
7. Piegl L., Tiller W. The NURBS Book (Monographs in Visual Communication), 2nd ed. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1997
8. Bajaj C., Chen J., Xu G. “Modeling with Cubic A-Patches.” ACM Transactions on Graphics, vol. 14, 103–133, 1995
9. Sederberg T.W., Cardon D.L., Finnigan G.T., North N.S., Zheng J., Lyche T. “T-Spline Simplification and Local Refinement.” ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), SIGGRAPH, vol. 23, 276–283, 2004
10. Cirak F., Scott M.J., Antonsson E.K., Ortiz M., Schröder P. “Integrated modeling, finiteelement analysis, and engineering design for thin-shell structures using subdivision.” Computer-Aided Design, vol. 34, 137–148, 2002
11. Blacker T. “A New Approach to Automated Quadrilateral Mesh Generation.” Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng, vol. 32, 811–847, 1991
12. Cook W.A., Oakes W.R. “Mapping methods for generating three-dimensional meshes.” Computers in Mechanical Engineering, pp. 67–72, 1982
13. “CUBIT Mesh Generation Toolkit. Web site: http://sass1693.sandia.gov/cubit.”
14. Blacker T. “The Cooper Tool.” 5th International Meshing Roundtable, pp. 13–29. 1996
15. Shepherd J., Mitchell S., Knupp P., White D. “Methods for MultiSweep Automation.”
16. Knupp P. “Next-Generation Sweep Tool: A Method for Generating All-Hex Meshes on Two-And-One-Half Dimensional Geometries.” 7th International Meshing Roundtable, pp. 505–513, 1998
17. White D., Saigal S., Owen S. “Automatic Decomposition of Multi-Sweep Volumes.” Engineering With Computers, vol. 20, 222–236, 2004
18. Staten M., Canaan S., Owen S. “BMSweep: Locating Interior Nodes During Sweeping.” 7th International Meshing Roundtable, pp. 7–18, 1998
19. Scott M., Earp M., Benzley S. “Adaptive Sweeping Techniques.” 14th International Meshing Roundtable, pp. 417–432, 2005
20. Armstrong C., Robinson D., McKeag R., Li T., Bridgett S., Donaghy R., McGleenan C. “Medials for Meshing and More.” 4th Int. Meshing Roundtable, pp. 277–288, 1995
21. Price M.A., Armstrong C.G., Sabin M.A. “Hexahedral Mesh Generation by Medial Surface Subdivision: I. Solids with Convex Edges.” Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng., vol. 38, 3335–3359, 1995
22. Storti D., Turkiyyah G., Ganter M., Lim C., Stal D. “Skeleton-based modeling operations on solids.” ACM Symposium Solid Modeling Applications, pp. 141–154, 1997
23. Quadros W.R., Owen S.J., Brewer M., Shimada K. “Finite Element Mesh Sizing for Surfaces Using Skeleton.” 13th International Meshing Roundtable, pp. 389–400, 2004
24. Zhang Y., Bajaj C., Sohn B.S. “3D Finite Element Meshing from Imaging Data.” The special issue of Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering (CMAME) on Unstructured Mesh Generation, vol. 194, no. 48–49, 5083–5106, 2005
25. Zhang Y., Bajaj C. “Adaptive and Quality Quadrilateral/Hexahedral Meshing from Volumetric Data.” Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering (CMAME), vol. 195, no. 9–12, 942–960, 2006
26. Ito Y., Shum P.C., Shih A., Soni B., Nakahashi K. “Robust generation of high-quality unstructured meshes on realistic biomedical geometry.” Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng., vol. 65, 943–973, 2006
27. Zachariah S.G., Sanders J.E., Turkiyyah G.M. “Automated Hexahedral Mesh Generation from Biomedical Image Data:Applications in Limb Prosthetics.” IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 4, no. 2, 91–102, 1996
28. Verma C.S., Fischer P.F., Lee S.E., Loth F. “An All-Hex Meshing Strategy for Bifurcation Geometries in Vascular Flow Simulation.” 14th International Meshing Roundtable, pp. 363–375, 2005
29. Thompson J.F., Soni B.K., Weatherill N.P. Grid Generation. CRC Press LLC, 1999
30. Gursoy H.N. “Tetrahedral Finite Element Mesh Generation from NURBS Solid Models.” Engineering with Computers, vol. 12, no. 19, 211–223, 1996
31. Anderson C.W., Crawford-Hines S. “Fast Generation of NURBS Surfaces from Polygonal Mesh Models of Human Anatomy.” Technical Report CS-99-101, Colorado State University, 2000
32. Yu T.Y., Soni B.K. “NURBS Evaluation and Utilization for Grid Generation.” 5th International Conference on Numerical Grid Generation in Computational Field Simulations, pp. 323–332, 1996
33. Yu Z., Bajaj C. “A Fast and Adaptive Algorithm for Image Contrast Enhancement.” IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP'04), vol. 2, pp. 1001–1004, 2004
34. Bajaj C., Wu Q., Xu G. “Level Set Based Volumetric Anisotropic Diffusion.” ICES Technical Report 301, the Univ. of Texas at Austin, 2003
35. Tomasi C., Madcuchi R. “Bilateral filtering for gray and color images.” IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, p. 839, 1998
36. Yu Z., Bajaj C. “Image Segementation using Gradient Vector Diffusion and Region Merging.” 16th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, vol. 2, pp. 941–944, 2002
37. Lorensen W., Cline H. “Marching Cubes: A High Resolution 3D Surface Construction Algorithm.” SIGGRAPH, pp. 163–169, 1987
38. Ju T., Losasso F., Schaefer S., Warren J. “Dual Contouring of Hermite Data.” SIGGRAPH, pp. 339–346, 2002
39. Goswami S., Dey T.K., Bajaj C.L. “Identifying Flat and Tubular Regions of a Shape by Unstable Manifolds.” 11th ACM Sympos. Solid and Physical Modeling, to appear, 2006
40. Hughes T.J.R. The Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element Analysis. Dover Publications, Mineola, NY, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Y., Bazilevs, Y., Goswami, S., Bajaj, C.L., Hughes, T.J. (2006). Patient-Specific Vascular NURBS Modeling for Isogeometric Analysis of Blood Flow. In: Pébay, P.P. (eds) Proceedings of the 15th International Meshing Roundtable. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-34958-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-34958-7_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-34957-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-34958-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)