Abstract
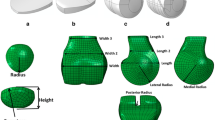
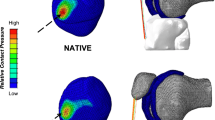
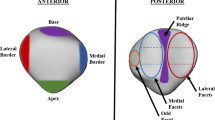
The outcome of patellofemoral joint reconstructive surgery has been found to be variable. This study presents patient-specific models of the patellofemoral joints of 13 patients diagnosed with osteoarthritis. The model is a mathematical model using quasi-static equilibrium analysis and the model inputs are patient data is acquired from a combination of two series of magnetic resonance images. Four tibial tuberosity transfer surgeries are simulated for each patient, namely: 15 mm anterior shift, 20 mm anterior shift, 8 mm anterior along with 8 mm medial shift, and 15 mm anterior along with 8 mm medial shift. The simulated surgeries produced a statistically significant decrease in mean contact stress relative to pre-surgical conditions (p=0.004), though no statistical difference was found between the different procedures. No one procedure consistently demonstrated the best outcome for all patients. In fact, certain surgical procedures increased peak stresses in some subjects while decreasing it in others. With the demonstrated variability of outcome, the utility of the model presented for surgical planning becomes apparent.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
References
Ahmed, A.M., Burke, D.L., Yu, A.: In-vitro measurement of static pressure distribution in synovialjoints—Part II: Retropatellar surface. J. Biomech. Eng. 105, 226–236 (1983)
Andriacchi, T.P., Natarajan, R.N., Hurwitz, D.E.: Musculoskeletal Dynamics, Locomotion, and Clinical Applications. In: Mow, V.C., Hayes, W.C. (eds.) Basic Orthopaedic Biomechanics, pp. 51–92. Raven Press, New York (1991)
Ateshian, G.A., Kwak, S.D., Soslowsky, L.J., Mow, V.C.: A stereophotograrnmetric method for determining in situ contact areas in diarthrodial joints, and a comparison withother methods. J. Biomech. 27, 111–124 (1994)
Benvenuti, J.F., Rakotomanana, L., Leyvraz, P.F., Pioletti, D.P., Heegaard, J.H., Genton, M.G.: Displacements of the tibial tuberosity. Effects of the surgical parameters. Clin. Orthop., 224–234 (1997)
Cohen, Z.A., Ateshian, G.A.: The Effect of Cartilage Layer Thickness on Patellofemoral Joint Kinematics and Contact Stresses. ASME Adv. in Bioeng. BED (1999)
Cohen, Z.A., Kwak, S.D., Ateshian, G.A., Blankevoort, L., Henry, J.H., Grelsamer, R.P., et al.: The effects of tibial tuberosity transfer on the patellofemoral joint: A 3-D simulation. ASME Adv. in Bioeng. BED 33, 387–388 (1996)
Cohen, Z.A., McCarthy, D.M., Kwak, S.D., Legrand, P., Fogarasi, F., Ciaccio, E.J., et al.: Knee cartilage topography, thickness, and contact areas from MRI: in-vitro calibration and in-vivo measurements. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 7, 95–109 (1999)
Cohen, Z.A., McCarthy, D.M., Roglic, P.L., Henry, J.H., Rodkey, W.G., Steadman, J.R., et al.: Computer-Aided Planning of Patellofemoral Joint OA Surgery: Developing Physical Models from Patient MRI. In: Wells, W.M.C.A., Delp, S. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, pp. 9–20. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
Farahmand, F., Senavongse, W., Amis, A.A.: Quantitative study of the quadriceps muscles and trochlear groove geometry related to instability of the patellofemoral joint. J. Orthop. Res., 136–143 (1998)
Ferguson Jr., A.B., Brown, T.D., Fu, F.H., Rutkowski, R.: Relief of patellofemoral contact stress by anterior displacement of the tibial tubercle. J. Bone Joint Surg. [Am] 61, 159–166 (1979)
Ferrandez, L., Usabiaga, J., Yubero, J., Sagarra, J., de No, L.: An experimental study of the redistribution of patellofemoral pressures by the anterior displacement of the anterior tuberosity of the tibia. Clin. Orthop., 183–189 (1989)
Fulkerson, J.P., Becker, G.J., Meaney, J.A., Miranda, M., Folcik, M.A.: Anteromedial tibial tubercle transfer without bone graft. Am J. Sports Med. 18, 490–496 (1991) (discussion 496-507)
Heatley, F.W., Allen, P.R., Patrick, J.H.: Tibial tubercle advancement for anterior knee pain. A temporary or permanent solution. Clin. Orthop. 208, 215–224 (1986)
Hirokawa, S.: Three-dimensional mathematical model analysis of the patellofemoral joint. J. Biomech. 24, 659–671 (1991)
Kwak, S.D., Ahmad, C.S., Gardner, T.R., Grelsamer, R.P., Henry, J.H., Blankevoort, L., et al.: Hamstrings and iliotibial band forces affect knee kinematics and contact pattern. J. Orthop. Res. 18, 101–118 (2000)
Kwak, S.D., Blankevoort, L., Ateshian, G.A.: A 3D quasi-static mathematical multibody model for diarthrodial joints. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering (October 2000)
Lewallen, D.G., Riegger, C.L., Myers, E.R., Hayes, W.C.: Effects of retinacular release and tibial tubercle elevation in patellofemoral degenerative joint disease. J. Orthop. Res. 8, 856–862 (1990)
Maquet, P.: Advancement of the tibial tuberosity. Clin. Orthop., 225–230 (1976)
Noll, B.J., Ben-Itzhak, I., Rossouw, P.: Modified technique for tibial tubercle elevation with realignment for patellofemoral pain. A preliminary report. Clin. Orthop. 234, 178–182 (1988)
Roglic, H., Ateshian, G.A., Cohen, Z.A., Kwak, S.D., Gardner, T., Henry, J., et al.: A Computer Simulation of Tibial Tuberosity Elevation and Patellar Tendon Adhesions. Trans. ORS 23, 617 (1998)
Schmid, F.: The Maquet procedure in the treatment of patellofemoral osteoarthrosis. Long-term results. Clin. Orthop., 254–258 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cohen, Z.A., Ateshian, G.A. (2000). Simulation of Patellofemoral Joint Reconstruction Surgery on Patient-Specific Models. In: Delp, S.L., DiGoia, A.M., Jaramaz, B. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2000. MICCAI 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1935. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-40899-4_112
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-40899-4_112
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-41189-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-40899-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive