Abstract
The intravascular neurosurgery is one of the most successful minimally invasive surgery. However, the difficulty to operate a catheter inside the cranial blood vessels because of the complexity and narrowness of blood vessels checks increasing the number of well-skilled doctors. Moreover the X-ray camera, which is used during an operation, causes the X-ray exposure to a doctor. One of the solution to these problems is telesurgery system.
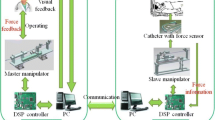
A novel telesurgery system for intravascular neurosurgery is described in this paper. This system has three main components; 1) A micro force sensor which can be installed in the catheter tip, and it measures a contact force between the catheter tip and a blood vessel wall. 2) A catheter teleoperation system which enables a surgeon to perform a medical operation to a patient from a distant place. 3) A force display strategy to improve operability and safety during an operation.
An in-vitro teleoperation experiment in the intravascular operating room is also performed and the effectiveness of the telesurgery system is confirmed.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
References
Arai, F., et al.: Multimedia Tele-surgery Using High Speed Optical Fiber Network and Its Application to Intravascular Neurosurgery. In: Proc. IEEE Int’l Conf. on Robotics and Automation ICRA 1996, vol. 1, pp. 878–883 (1996)
Mitsuishi, M., Iizuka, Y., Nakanishi, H., et al.: Remote operation of a micro surgical System. In: Proc. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1013–1019 (1998)
Salcudean, S.E., et al.: Performance Measurement in Scaled Teleoperation for Microsurgery. In: Troccaz, J., Mösges, R., Grimson, W.E.L. (eds.) CVRMed-MRCAS 1997, CVRMed 1997, and MRCAS 1997. LNCS, vol. 1205, pp. 789–798. Springer, Heidelberg (1997)
Hill, J.W.: Telepresence Surgery Demonstration System. In: Proc. 1994 IEEE Int’l Conf. on Robotics and Automation, vol. 3, pp. 2302–2307 (1994)
Tanimoto, M., et al.: Augmentation of Safety in Teleoperation System for Intravascular Neurosurgery. In: IEEE Int’l Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2890–2895 (1998)
Tanimoto, M., et al.: Micro Force Sensor for Intravascular Neurosurgery. In: IEEE Int’l Conf. on Robotics and Automation, vol. 2, pp. 1561–1566 (1997)
Kwon, K.S., et al.: A Robot with Improved Adcolute Positioning Accuracy for CT Guided Stereotactic Surgery. IEEE Trans. on Biomedical Engineering, 153–161 (February 1988)
Salcudean, S.E., Yen, J.: Towards a Force-reflecting Motion-Scaling System for Microsurgery. In: Proc. 1994 IEEE Int’l Conf. on Robotics and Automation, vol. 3, pp. 2296–2301 (1994)
Kaneko, K., et al.: Impedance Shaping based on Force Feedback Bilateral Control in Macro-Micro Teleoperation System. In: IEEE Int’l Conf. on Robotics and Automation, vol. 1, pp. 710–717 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tanimoto, M. et al. (2000). Telesurgery System for Intravascular Neurosurgery. In: Delp, S.L., DiGoia, A.M., Jaramaz, B. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2000. MICCAI 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1935. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-40899-4_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-40899-4_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-41189-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-40899-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive