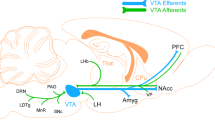
Abstract
We present a computational model, based on formal reinforcement learning theory, that offers an explanation for why dopamine blockade leads to attenuation of the avoidance response in the animal experimental paradigm: Conditioned Avoidance Response (CAR). Since the CAR paradigm is used to screen for antipsychotic drug efficacy, we hope to extend our model to provide an explanation of how dopamine dysregulation leads to psychosis. We are also currently extending the model to an explanation of other dopamine related dysfunctions including impulsivity, and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge, K.C., Robinson, T.E.: What is the role of dopamine in reward: hedonic impact, reward learning, or incentive salience? Brain Research Reviews 28, 309–369 (1998)
Braver, T.S., Barch, D.M., Cohen, J.D.: Cognition and control in schizophrenia: Acomputational model of dopamine and prefrontal function. Biological psychiatry 46, 312–328 (1999)
Cooper, J.R., Bloom, F.E., Roth, R.H.: The biochemical basis of neuropharmacology, ch. 9. Oxford University Press, New York (1996)
Daw, N.D., Touretzky, D.: Long-term reward prediction in td models of dopamine system. Neural Computation 14, 2567–2583 (2002)
Dayan, P.: Motivated reinforcement learning (2002) (preprint)
Dayan, P., Balleine, B.W.: Reward, motivation and reinforcement learning. Neuron 36, 285–298 (2002)
de Wit, H., Enggasser, J.L., Richards, J.B.: Acute administration of d-amphetamine decreases impulsivity in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 27(5), 813–825 (2002)
DiChiara, G.: Drug addiction as dopamine-dependent associative learning disorder. European Journal of Pharmacology 375, 13–30 (1999)
Horvitz, J.C.: Dopamine gating of glutamatergic sensorimotor and incentive motivational input signals to the striatum. Behavioural Brain Research 137, 65–74 (2002)
Kandel, E.R., Schwartz, J.H., Jessell, T.M.: Principles of neural science. Elsevier Science, New York (1991)
Marie-Louise, G., Wadenberg, A.S., Vanderspek, S.C., Kapur, S.: Dopamine d2 receptor occupancy is a common mechanism underlying animal models of antipsychotics and their clinical effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 25(25), 633–641 (2001)
Salamone, J.D., Cousins, M.S., Snyder, B.J.: Behavioural functions of nucleus accumbens dopamine: empirical and conceptual problems with the anhedonia hypothesis. Neuroscience and Biobehavioural reviews 21(3), 341–359 (1997)
Schultz, W.: Dopamine neurons and their role in reward mechanisms. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 7(2), 191–197 (1997)
Schultz, W., Dayan, P., Montague, P.R.: An eural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275, 1593–1599 (1997)
Servan-Schreiber, D., Printz, H., Cohen, J.D.: A network model of catecholamine effects: gain, signal to noise ratio, and behavior. Science 249(4971), 892–895 (1990)
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge (1998)
Waelti, P., Dickinson, A., Schultz, W.: Dopamine responses comply with basic assumptions of formal learning theory. Nature 412, 43–48 (2001)
Williams, J., Dayan, P.: Dopamine, learning, and impulsivity: A biological account of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (2002)
Wise, R.A.: Neuroleptics and operant behavior: the anhedonia hypothesis. The Behavioural and Brain Sciences, 39–87 (1982)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Smith, A., Becker, S., Kapur, S. (2003). From Dopamine to Psychosis: A Computational Approach. In: Palade, V., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L. (eds) Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems. KES 2003. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 2774. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-45226-3_152
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-45226-3_152
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-40804-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45226-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive