Abstract
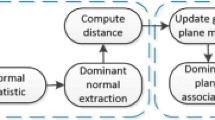
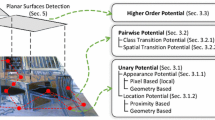
3d reconstruction from a single image is inherently an ambiguous problem. Yet when we look at a picture, we can often infer 3d information about the scene. Humans perform single-image 3d reconstructions by using a variety of single-image depth cues, for example, by recognizing objects and surfaces, and reasoning about how these surfaces are connected to each other. In this paper, we focus on the problem of automatic 3d reconstruction of indoor scenes, specifically ones (sometimes called “Manhattan worlds”) that consist mainly of orthogonal planes. We use a Markov random field (MRF) model to identify the different planes and edges in the scene, as well as their orientations. Then, an iterative optimization algorithm is applied to infer the most probable position of all the planes, and thereby obtain a 3d reconstruction. Our approach is fully automatic—given an input image, no human intervention is necessary to obtain an approximate 3d reconstruction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Besag. Spatial interaction and the statistical analysis of lattice systems. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 1974.
J. Canny. A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 8(6):679–698, 1986.
J. Coughlan and A.L. Yuille. Manhattan world: Compass direction from a single image by bayesian inference. In IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 1999.
J. Coughlan and A.L. Yuille. Manhattan world. Neural Computation, 15:1063–1088, 2003.
A. Criminisi, I. Reid, and A. Zisserman. Single view metrology. International Journal of Computer Vision, 40:123–148, 2000.
P. E. Debevec, C. J. Taylor, and J. Malik. Modeling and rendering architecture from photographs. In SIGGRAPH, 1996.
E. Delage, H. Lee, and A. Y. Ng. A dynamic Bayesian network model for autonmous 3d reconstruction from a single indoor image. Unpublished manuscript, 2005.
P. Favaro and S. Soatto. Shape and radiance estimation from the information divergence of blurred images. In European Conference on Computer Vision, 2000.
Pedro F. Felzenszwalb and Daniel P. Huttenlocher. Efficient graph-based image segmentation. International Journal of Computer Vision, 59, 2004.
R. C. Gonzalez and R. E. Woods. Digital Image Processing. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc., Boston, MA, USA, 1992.
F. Han and S. C. Zhu. Bayesian reconstruction of 3d shapes and scenes from a single image. In IEEE International Workshop on Higher-Level Knowledge in 3D Modeling and Motion Analysis, pages 12–20, 2003.
F. Huang and Y. Ogata. Generalized pseudo-likelihood estimates for Markov random fields on lattice. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 2002.
A. Kosaka and A. C. Kak. Fast vision-guided mobile robot navigation using model-based reasoning and prediction of uncertainties. CVGIP: Image Understanding, 56:271–329, 1992.
J. Kosecka and W. Zhang. Video compass. In European Conference on Computer Vision, 2002.
P. Kovesi. Image features from phase congruency. Videre: A Journal of Computer Vision Research, 1, 1999.
P. D. Kovesi. MATLAB and Octave functions for computer vision and image processing. School of Computer Science & Software Engineering, The University of Western Australia. Available from: http://www.csse.uwa.edu.au/~pk/research/matlabfns/.
E. Lutton, H. Maitre, and J. Lopez-Krahe. Contribution to the determination of vanishing points using hough transform. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 16:430–438, 1994.
J. Michels, A. Saxena, and A. Y. Ng. High-speed obstacle avoidance using monocular vision and reinforcement learning. In International Conference on Machine Learning, 2005.
A. Saxena, S. Chung, and A. Y. Ng. Learning depth from single monocular images. In Neural Information Processing Systems, 2005.
G. Schindler and F. Dellaert. Atlanta World: An expectation-maximization framework for simultaneous low-level edge grouping and camera calibration in complex man-made environments. In IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2004.
H.-Y. Shum, M. Han, and R. Szeliski. Interactive construction of 3d models from panoramic mosaics. In IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1998.
P. F Sturm and S. J. Maybank. A method for interactive 3d recontruction of piecewise planar objects from single images. In British Machine Vision Conference, 1999.
C. Tomasi and T. Kanade. Shape and motion from image streams under orthography: a factorization method. International Journal of Computer Vision, 9:137–154, 1992.
M. J. Wainwright, T. S. Jaakkola, and A. S. Willsky. Tree-based reparameterization framework for analysis of sum-product and related algorithms. IEEE Trans. Information Theory, 49(5):1120–1146, 2003.
R. Zhang, P.-S. Tsai, J. E. Cryer, and M. Shah. Shape from shading: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 21:690–706, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Delage, E., Lee, H., Ng, A.Y. (2007). Automatic Single-Image 3d Reconstructions of Indoor Manhattan World Scenes. In: Thrun, S., Brooks, R., Durrant-Whyte, H. (eds) Robotics Research. Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, vol 28. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-48113-3_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-48113-3_28
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-48110-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-48113-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)