Abstract
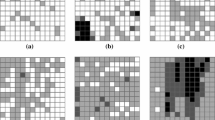
In this paper, extensions of the classification tree algorithm and analysis for spatial data are proposed. These extensions focus on: (1) a robust manner to prune a classification tree to smooth sampling (e.g., spatial sampling effects), (2) an assessment of tree spatial prediction performances with respect to its ability to satisfactorily represent the actual spatial distribution of the variable of interest, and (3) a unified framework to aid in the interpretation of the classification tree results due to variable correlations. These methodological developments are studied on an agricultural practices classification problem at an agricultural plot scale, specifically, the weed control practices on vine plots over a 75 km2 catchment in the South of France. The results show that, with these methodological developments, we obtain an explicit view of the uncertainty associated with the classification process through the simulation of the spatial distribution of agricultural practices. Such an approach may further facilitate the assessment of model sensitivities to categorical variable map uncertainties when using these maps as input data in environmental impact assessment modelling.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaron, B., Kromrey, J. D., & Ferron, J. M. (1998). Equating r-based and d-based effect-size indices: Problems with a commonly recommended formula. Annual meeting of the Florida Educational Research Association, Orlando, FL., ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED433353.
Aubry C., Papy F. and Capillon A. (1998). Modelling decision-making process for annual crop management. Agricultural Systems 56(1): 45-65.
Bel L., Laurent J.M. , Bar-Hen A., Allard D. and Cheddadi R. (2005). A spatial extension of CART: application to classification of ecological data, Geostatistics for environmental applications, Springer: Heidelberg, 99-109.
Biarnès A., Rio P. and Hocheux A. (2004). Analysing the determinants of spatial distribution of weed contol practices in a Languedoc vineyard catchment. Agronomie, 24: 187-191.
Bonfils P. (1993). Carte pédologique de France au 1/100°000 ; feuille de Lodève, SESCPF INRA.
Breiman L., Friedman J. H., Olshen R. A. and Stone C. J. (1984). Classification and Regression Tree. London, Chapman and Hall, 358 p.
Breiman L. (1996a). Bagging predictors. Machine learning 26(2): 123-140.
Breiman L. (1996b). Random forest. Machine learning 45: 5-32.
Bui, E., and Moran, C. (2001). Disaggregation of polygons of superficial geology and soil maps using spatial modelling and legacy data. Geoderma, 103: 79-94.
Chiffoleau Y. (2005). Learning about innovation through networks: the development of environment-friendly viticulture. Technovation 25(10): 1193-1204.
Cohen J. (1960). A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales, Educational and Psychological Measurement 20: 37–46.
Espa, G., Benedetti, R., De Meo, A., U. Ricci and Espa S. (2006). GIS based models and estimation methods for the probability of archaeological site location Journal of Cultural Heritage, 7(3), July,147-155
Fearer, T.M., Prisley, S.P., Stauffer; D.F., and Keyser P.D (2007). A method for integrating the Breeding Bird Survey and Forest Inventory and analysis databases to evaluate forest bird–habitat relationships at multiple spatial scales. Forest Ecology and Management, 243(1), 128-143
Gellrich, M., Baur, P., Robinson, B.H. and Bebi P. (2008). Combining classification tree analyses with interviews to study why sub-alpine grasslands sometimes revert to forest: A case study from the Swiss Alps, Agricultural Systems, 96(1-3), 124-138
Geurts P., Ernst D. and Wehenkel L. (2006). Extremely randomized trees. Machine learning 63: 3 - 42.
Gini C. (1912). Variabilità e mutabilità. Memorie di metodologica statistica. Vol. 1, E. Pizetti and T. Salvemini. Rome, Libreria Eredi Virgilio Veschi, pp 211-382
Goovaerts P. (2001). Geostatistical modelling of uncertainty in soil science. Geoderma 103: 3-26.
Haase, R.C. (1983). Classical and Partial Eta Square in Multifactor ANOVA Designs. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 43(1), 35-39.
Hébrard O., Voltz M., Andrieux P. and Moussa R. (2006). Spatio-temporal distribution of soil surface moisture in a heterogeneously farmed Mediterranean catchment. Journal of Hydrology 329: 110-121.
Ihaka R. and Gentleman R. (1996). R: A Language for Data Analysis and Graphics,. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 5(3): 299-314.
Lagacherie, P. and Holmes, S. (1997). Addressing geographical data errors in a classification tree for soil unit prediction. Int. J. Geographical Info. Sci. 11, pp. 183–198
Lennartz B., Louchard X., Voltz M. and Andrieux P. (1997). Diuron and simazine losses to runoff water in mediterranean vineyards. Journal of Environmental Quality 26(6): 1493-1502.
Leonard J. and Andrieux P. (1998). Infiltration characteristics of soils in Mediterranean vineyards in Southern France. Catena 32: 209-223.
Louchart X., Voltz M., Andrieux P. and Moussa R. (2001). Herbicide Transport to Surface Waters at Field and Watershed Scales in a Mediterranean Vineyard Area. Journal of Environmental Quality 30: 982-991.
McDonald, R.I., Urban, D.L. (2006). Spatially varying rules of landscape change: lessons from a case study, Landscape and Urban Planning, 74(1), 7-20.
Mahalanobis P. C. (1936). On the generalised distance in statistics. Proceedings of the National Institute of Science of India 12: 49-55.
Ripley B. (2007). Pattern recognition and neural Networks. Cambrige, Cambridge University Press, 415 p.
Schröder W., (2006). GIS, geostatistics, metadata banking, and tree-based models for data analysis and mapping in environmental monitoring and epidemiology, International Journal of Medical Microbiology, Volume 296(1-22 ), 23-36.
Tittonell, P., Shepherd, K.D. , Vanlauwe, B. and Giller, K.E. (2008) Unravelling the effects of soil and crop management on maize productivity in smallholder agricultural systems of western Kenya—An application of classification and regression tree analysis, Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 123(1-3), 137-150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bailly, J.S., Biarnes, A., Lagacherie, P. (2008). Spatial Simulation of Agricultural Practices using a Robust Extension of Randomized Classification Tree Algorithms. In: Ruas, A., Gold, C. (eds) Headway in Spatial Data Handling. Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-68566-1_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-68566-1_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-68565-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-68566-1
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)