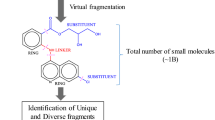
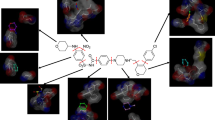
Abstract
In molecular fragments mining, scientists use both manual techniques and pure computer based methods. In this paper, we propose a novel molecular fragment mining approach that incorporates interactive user assistance to speed up and increase the success rates in traditional fragment mining processes. The proposed approach visualizes 3D molecular data in 2D form that can be easily interpreted by a human expert who evaluates and filters the 2D molecular images manually. The proposed approach differs from others in literature as it does not search substructures including specific atoms like graph mining methods do. Instead, user assisted approach highlights significant substructures with specific properties and topologies graphically. Initial experiments indicate that by the use of user assisted approach, active and inactive fragments of compounds are quickly determined for drug design with high success rates.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, A., Wang, Y.: Comparison of Classification Methods for Screening Potential Compounds. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2001)
Stenberg, M.J.E., Muggleton, S.H.: Structure Activity Relationships (SAR) and Pharmacophore Discovery Using Inductive Logic Programming (ILP). QSAR Comb. Sci. 22 (2003)
Fischer, I., Meinl, T.: Graph Based Molecular Data Mining – An Overview. IEEE international Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (2004)
Yang, G.: The Complexity of Mining Maximal Frequent Itemsets and Maximal Frequent Patterns. In: ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining (2004)
Cook, J., Holder, L.: Substructure discovery using minimum description length and background knowledge. J. Artificial Intel. Research 1, 231–255 (1994)
Inokuchi, A., Washio, T., Motoda, H.: Complete mining of frequent patterns from graphs:Mining graph data. Machine Learning 50, 321–354 (2003)
Kuramochi, M., Karypis, G.: Frequent subgraph discovery. In: ICDM 2001: 1st IEEE Conf. Data Mining, pp. 313–320 (2001)
Yan, X., Han, J.: gspan: Graph-based substructure pattern mining. In: ICDM 2002: 2nd IEEE Conf. Data Mining, pp. 721–724 (2002)
Deshpande, M., Kuramochi, M., Wale, N., Karypis, G.: Frequent Substructure-Based Approaches for Classifying Chemical Compounds. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 17(8) (2005)
van der Heijden, F., Duin, R.P.W., de Ridder, D., Tax, D.M.J.: Classification, Parameter Estimation and State Estimation. Wiley, Chichester (2004)
Shvets, N., Dimoglo, A.S.: The Electron-topological method (ETM): Its further development and use in the problems of SAR study. In: Molecular modeling and prediction of bioactivity, pp. 418–429. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York (1999)
Baker, H.: Computer Graphics, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2003)
Alpaydın, E.: Introduction to Machine Learning, 1st edn. MIT Press, Cambridge (2001)
Xu, R., Wunsch, D.: Survey of Clustering Algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 16(3) (May 2005)
Nayyar, A., Monga, V., Malde, A., Coutinho, E., Jain, R.: Synthesis, anti-tuberculosis activity and 3D-QSAR study of 4-(adamantan-1-yl)-2-substituted quinolines. Bioorganic&Medicinal Chemistry 15, 626–640 (2007)
Nijssen, S., Kok, J.N.: Frequent Graph Mining and its Application to Molecular Databases. In: IEEE International SMC (2004)
Molinara, M., Riamato, M.T., Tortorello, F.: Facing imbalanced classes through aggregation of classifiers. In: IEEE ICIAP 2007, pp. 43–48 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yılmaz, B., Göktürk, M., Shvets, N. (2008). User Assisted Substructure Extraction in Molecular Data Mining. In: Perner, P., Salvetti, O. (eds) Advances in Mass Data Analysis of Images and Signals in Medicine, Biotechnology, Chemistry and Food Industry. MDA 2008. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 5108. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-70715-8_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-70715-8_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-70714-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-70715-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)