Abstract
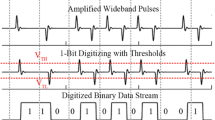
Low power on-body communication is introduced. The human body surface is examined for the communication channel and 10KHz-100MHz frequency band, ‘bodywire’, is found to be effective in the wireless on-body communication. DCI is proposed to avoid any intentional ground electrode for the capacitive coupling. A CMOS transceiver chip for the on-body communication is fabricated and can achieve 2Mbps with 0.2mW power consumption. The architecture of the BSN controller is proposed and fabricated with CMOS. It has a 16b RISC and a schedule director with TCAM. It can separately control 254 sensor nodes and consumes 14uW in normal mode and 160uW in alert mode including leakage current. The fabricated chip is used to transmit MP3 data from the finger tip to the earphone to enjoy the music. In addition, the BSN controller can detect the emotion of the user by using the data from the sensor nodes transmitted through on-body communication channel.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Ashok and D. Agrawal, “Next-Generation Wearable Netwoks”, IEEE Computer, pp. 31–39, Nov. 2003.
S.-J. Song, et al., “A 2Mb/s Wideband Pulse Transceiver with Direct-Coupled Interface for Human Body Communications,” ISSCC Dig. Tech. Papers, pp. 558–559, Feb., 2006.
J. Ryckaert, et al., “A 16mA UWB 3-to-5GHz 20Mpulses/s Quadrature Analog Correlation Receiver in 0.18um CMOS,” ISSCC Dig. Tech. Papers, pp. 114–115, Feb. 2006
T. G. Zimmerman, “Personal area networks: Near-field intrabody communication,” IBM Syst. J., vol. 35, no. 3–4, pp. 609–617, 1996..
K. Hachisuka, et al., “Development and Performance Analysis of an Intra-Body Communication Device,” Transducers’ 03, pp. 1722–1725, June 2003
M. Shinagawa, et al., “A Near-Field-Sensing Transceiver for Intrabody Communication Based on the Electrooptic Effect,” IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., vol. 53, pp. 1533–1538, Dec. 2004.
N. Cho, et al, “The Human Body Chracteristics as a Signal Transmission Medium for Intra Body Communication,” Trans. Microwave Teory and Techniques, Submitted.
S.-J. Song, et al., “A 4.8mW 10Mb/s Wideband Signaling Receiver Analog Front-End for Human Body Communications,” Proc. ESSCIRC, pp. 488–491, Sep, 2006.
Sungdae Choi et al, “A 24.2-µW Dual-Mode Human Body Communication Controller for Body Sensor Network” ESSCIRC Dig. Tech. Papers, pp.227–230, Sep. 2006.
Sungdae Choi et al, “A TCAM based Periodic Event Generator for Multi-node Management in Body Sensor Network,” Proc. ASSCC 2006, pp.307–310, Nov. 2006.
Heyjeong Kim, et al, “A Low Power 16bit RISC with Lossless Compression Accelerator for Body Sensor Network System,” Proc. ASSCC 2006, pp.207–210, Nov. 2006.
R. W. Picard, et al, “Toward Machine Emotional Intelligence: Analysis of Affective Physiological State,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, pp. 1175–1190, Oct. 2001.
Heyjeong Kim, et al, “A Low Power Sensor Node Controller for Human Body Monitoring,” Journal of Korean Institute of Next Generation Computing, pp.14–20, Vol.2, No. 3, Sep. 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yoo, HJ., Song, SJ., Cho, N., Kim, HJ. (2007). Low Energy On-Body Communication for BSN. In: Leonhardt, S., Falck, T., Mähönen, P. (eds) 4th International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN 2007). IFMBE Proceedings, vol 13. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-70994-7_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-70994-7_3
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-70993-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-70994-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)