Abstract
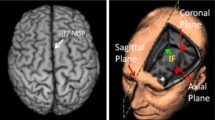
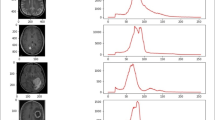
We present the simple and fast symmetry plain detection algorithm, that recognizes Falx cerebri curve on each human brain computed thomogrpahy slice. Symmetry curves appear approximately on 30% images and using such images as reference it is possible to determine symmetry plane. We propose an algorithm based on hybrid methods, that allows detect symmetry plane with deviation angle until 25º. The method is based on fuzzy logic that selects region of interest and symmetry curves. Direct pixels selection with evaluation of symmetry curve properties are used to calculate symmetry plane with high speed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prima S, Ourselin S, Ayache N. Computation of the mid-sagittal plane in 3D brain images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2002; 122–138.
Tuzikov AV, Colliot O, Bloch I. Brain symmetry plane computation in MR images using inertia axes and optimization. Institute of Engineering Cybernetics Academy of Sciences of Republic Belarus: IEEE; 2002. 1051–4651.
Ardekani BA, Kershaw J, Braun M, Kanuo I. Automatic detection of the midsagittal plane in 3D brain images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1997;16:947–952.
Liu Y, Collins RT, Rothfus WE. Robust midsagittal plane extraction from normal and pathological 3D neuroradiology images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2001;20:175–192.
Brummer ME. Hough transform detection of the longitudinal fissure in tomographic head images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1991;10:74–81.
Anbazhagan P, Carass A, Bazin P, Prince JL. Automatic estimation of midsagittal plane and AC-PC alignment based on nonrigid registration. Procs IEEE Symp Biomed Imaging 2006; 828–831.
Prima S, Ourselin S, Ayache N. Computation of the mid-sagittal plane in 3D brain images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2002;21:122–138.
Smith S, Jenkinson M. Accurate robust symmetry estimation. Procs MICCAI 1999; 308–317.
Grigaitis D, Zitkevicius E, Usinskas A. Determination of symmetry axis on human brain CT image. Procs Bienlial Baltic Electronics Conf 2004; 165–168.
Gonzalez RC, E WoodsR. Digital Image Processing. Prentice-Hall, Inc.-Second Edition; 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Grigaitis, D., Meilunas, M. (2007). Automatic Extraction of Symmetry Plane from Falx Cerebri Areas in CT Slices. In: Horsch, A., Deserno, T.M., Handels, H., Meinzer, HP., Tolxdorff, T. (eds) Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2007. Informatik aktuell. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71091-2_54
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71091-2_54
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-71090-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-71091-2
eBook Packages: Computer Science and Engineering (German Language)