Abstract
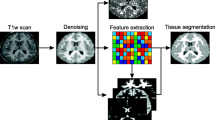
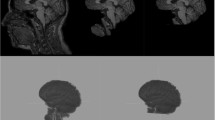
A novel model-based identification of white brain matter in OCT A-scans is proposed. Based on nonlinear energy operators used in the classification of neural activity, candidates for white matter structures are extracted from a baseline-corrected signal. Validation of candidates is done by evaluating the correspondence to a simplified intensity model which is parametrized beforehand. Results for identification of white matter in rat brain in vitro show the capability of the proposed algorithm.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouma BE, Tearney GJ. Handbook Of Optical Coherence Tomography. Marcel Dekker, Inc.; 2002.
Boehringer HJ, Boller D, Leppert J, et al. Time-domain and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in the analysis of brain tumor tissue. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 2006;38:588–597.
Jeon SW, Shure MA, Baker KB, etal. Optical coherence tomography and optical coherence domain reflectometry for deep brain stimulation probe guidance. Procs SPIE 2005;5686:487–494.
Safri MS, Farhang S, Tang RS, et al. Optical coherence tomography in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders. J Biomed Opt 2005;10(5):1–11.
Kim KW, Kim SJ. Neural spike sorting under nearly 0-dB signal-to-noise ratio using nonlinear energy operator and artificial neural-network classifier. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2000;47:1406–1411.
Menne KL. Computerassistenz zur Implantation von Tiefenhirnstimulatoren. Ph.D. thesis. University of Luebeck; 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ramrath, L., Hofmann, U.G., Huettmann, G., Moser, A., Schweikard, A. (2007). Towards Automated OCT-based Identification of White Brain Matter. In: Horsch, A., Deserno, T.M., Handels, H., Meinzer, HP., Tolxdorff, T. (eds) Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2007. Informatik aktuell. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71091-2_83
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71091-2_83
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-71090-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-71091-2
eBook Packages: Computer Science and Engineering (German Language)