Abstract
Landscape fragmentation is a major threat to a lot of wildlife species with a large spatial activity range. To ease the migration through the landscape, a lot of different measurements can be implemented. Though, due to limited resources, these should be placed where they are most effective.
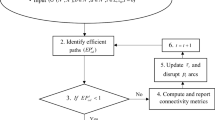
The simulation framework SimapD presented in this paper is capable of assessing the network permeability and incorporates effects of anthropogenic obstacles, like roads, into the assessment. Through an individual-oriented simulation an overall permeability index for a habitat network is obtained. Based on this simulation approach, an algorithm is presented for optimizing such habitat networks concerning its permeability. It is intended to be applied to find optimal mitigation strategies. The complete procedure is illustrated by an example.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baier H, Erdmann F, Holz R, Waterstraat A (eds) (2006) Freiraum und Naturschutz: Die Wirkung von Störungen und Zerschneidungen in der Landschaft. Springer, Berlin
Finke J (in press) Ein Simulationsframework zur Bewertung von großräumigen Habitatnetzen. Modellierung und Simulation von Ökosystemen — Workshop Kölpinsee 2006
Finke J, Strein M, Sonnenschein M (submitted) A Simulation Framework for Modelling Anthropogenic Disturbances in Habitat Networks, submitted to Ecological Informatics, Special Issue 3: Bioinspired Computation and Hybrid Modelling of Aquatic and Terrestrial Ecosystems
Forman RTT (2003) Land Mosaics: The ecology of landscape and regions. Cambridge University Press
Forman RTT and Sperling D (2002) Road Ecology: Science and Solutions. Island Press
Grüning F, Sonnenschein M (2005) A Method for Optimizing a Metapopulation. In: Leal Filho W, Marx Gómez J, Rautenstrauch C (eds) ITEE 2005-Second International ICSC Symposium on Information Technologies in Environmental Engineering. ISBN 3-8322-4362-3, pp 365–380
Hlaváč V (2005) Increasing Permeability of the Czech Road Network for Large Mammals. GAiA Themenschwerpunkt Landschaftszerschneidung, vol 14, edn 2, pp 175–177
Hsu CW, Chang CC, Lin CJ (2006) A practical guide to support vector classification. http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/papers/guide/guide.pdf, access: 2006-10-31
Jaeger JAG (2000) Landscape division, splitting index, and effective mesh size: New measures of landscape fragmentation Landscape Ecology, vol 15, edn 2, pp 115–130
McGarigal K, Chushman SA, Neel MC, Ene E (2002) FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorial Maps. http://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html, access: 2006-10-31
Michalewicz Z, Fogel DB (2000) How to Solve It: Modern Heuristics. Springer, Berlin
Oggier P, Righetti A, Bonnard L (eds) (2001) Zerschneidung von Lebensräumen durch Verkehrsinfrastrukturen COST 341. Bundesamt für Umwelt, Wald und Landschaft; Bundesamt für Raumentwicklung; Bundesamt für Verkehr; Bundesamt für Strassen, Bern
Smola AJ, Schölkopf B (1998) A Tutorial on Support Vector Regression. Neuro-COLT Technical Report NC-TR-98-030. Royal Holloway College, University of London, UK
Strein M, Müller U, Suchant R (2006) Artunspezifische Modellierung einer Korridor-Potenzial-Karte für Mitteleuropa — Methodik und erste Ergebnisse einer landschaftsökologischen GIS-Analyse. Naturschutz und biologische Vielfalt, vol 17
Trocmé M (2006) Habitat Fragmentation due to Linear Transportation Infrastructure: An overview of mitigation measures in Switzerland. 6th Swiss Transport Research Conference (STRC 2006) http://www.strc.ch/pdf_2006/Trocme_STRC_2006.pdf, access: 2006-10-31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Finke, J., Sonnenschein, M. (2007). Simulation and Optimization of Habitat Network Permeability. In: Gómez, J.M., Sonnenschein, M., Müller, M., Welsch, H., Rautenstrauch, C. (eds) Information Technologies in Environmental Engineering. Environmental Science and Engineering. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71335-7_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71335-7_44
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-71334-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-71335-7
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)