Summary
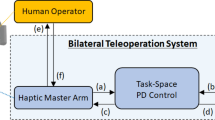
When dealing with teleoperated systems, several important aspects have to be considered: unstructured environment, communication delay, human operator uncertainty, and safety at the remote site, amongst others. The main contribution of this work, that tackles some of the aforementioned issues, is a system that combines a force feedback teleoperation scheme with geometric constraints and haptic guidance. The allowed motion space of a robot can be reduced by specifying a set of geometric relations between the robot tool and the workcell’s fixed objects. These relations are processed by a geometric reasoning module that generates a compatible motion subspace. Restriction forces are then fed to the operator via a haptic interface in order to guide its movements inside this subspace. The communication channel between the local center and the remote cell is implemented using high speed networks with the novel IPv6 protocol. The slave robot control is based on position or velocity. Experimental results validate the proposed approach.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.J. Unger, A. Nicolaidis, P.J. Berkelman, A. Thompson, S. Lederman, R.L. Klatzky, and R.L. Hollis. Virtual peg-in-hole performance using a 6-dof magnetic levitation haptic device: comparison with real forces and with visual guidance alone. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, pages 263–270, March 2002.
S. Shon and S. McMains. Evaluation of drawing on 3d surfaces with haptics. In IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 24(6):40–50, Nov.–Dec. 2004.
T.H. Massie and J.K. Salisbury. The phantom haptic interface: A device for probing virtual objects. In Proceedings of the ASME Winter Annual Meeting, Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, 55(1):295–300, Nov. 1994.
N. Turro, O. Khatib, and E. Coste-Maniere. Haptically augmented teleoperation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 1:386–392, May 2001.
A. Casavola and M. Sorbara. Towards constrained teleoperation for safe long-distance robotic surgical operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pages 697–702, 2005.
N. Diolaiti, G. Niemeyer, F. Barbagli, J.K. Salisbury, and C. Melchiorri. The effect of quantization and coulomb friction on the stability of haptic rendering. In First Joint Eurohaptics Conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, pages 237–246, March 2005.
J.E. Colgate, P.E. Grafing, M.C. Stanley, and G. Schenkel. Implementation of stiff virtual walls in force-reflecting interfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE Virtual Reality Annual International Symposium, pages 202–208, 1993.
P. Pan, K.M. Lynch, M.A. Peshkin, and J.E. Colgate. Static single-arm force generation with kinematic constraints. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 3:2794–2800, 2004.
T. Tickel, D. Hannon, K.M. Lynch, M.A. Peshkin, and J.E. Colgate. Kinematic constraints for assisted single-arm manipulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2:2034–2041, 2002.
E.S. Boy, E. Burdet, C.L. Teo, and Colgate. Motion guidance experiments with scooter cobot. In Proceedings of the 11th IEEE Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, 20(4):63–69, March 2003.
E.B. Fgee, J.D. Kenney, W.J. Phillips, W. Robertson, and S. Sivakumar. Comparison of qos performance between ipv6 qos management model and intserv and diffserv qos models. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE Annual Communication Networks and Services Research Conference, pages 287–292, May 2005.
IPv6. Ipv6 information page. http://www.ipv6.org/, 2005.
V. Srivastava, C. Wargo, and S. Lai. Aviation application over ipv6: performance issues. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Aerospace Conference, 3:1661–1670, March 2004.
P.X. Liu, M. Meng, and S. Yang. Data communications for internet robots. Kluwer Academic Autonomous Robots, 15(3):213–223, 2003.
R. Oboe. Web-interfaced, force-reflecting teleoperation systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 48(3):1257–1265, Dec. 2001.
S. Munir and W.J. Book. Internet-based teleoperation using wave variables with prediction. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 7(2):124–133, June 2002.
P.X. Liu, M. Meng, Y. Xiufen, and J. Gu. An UDP-based protocol for internet robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, 1:59–65, June 2002.
R. Safaric, S. Sinjur, B. Zalik, and R.M. Parkin. Control of robot arm with virtual environment via the internet. In Proceedings of the IEEE, 91(3):422–429, March 2003.
K. Taylor and B. Dalton. Internet robots: a new robotics niche. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 7(1):27–34, March 2000.
R.C. Luo, K.L. Su, S.H. Shen, and K.H Tsai. Networked intelligent robots through the internet: issues and opportunities. In Proceedings of the IEEE, 91(3):371–382, March 2003.
C.M. Hoffman and R. Joan-Arinyo. A brief on constraint solving. Unabridged version at http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/cmh/distribution/papers/Constraints/ThailandFull.pdf; abridged version to appear in CAD&A, pages 873–881, 2005.
E. Celaya. LMF: A program for positioning objects using geometrical relationships. In VII International Conference on Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Engineering. Elsevier Applied Science, pages 873–881, 1992.
F. Janabi-Sharifi, V. Hayward, and C-S.J Chen. Discrete-time adaptive windowing for velocity estimation. Control Systems Technology, IEEE Transactions on, 8(6):1003–1009, Nov. 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Nuño, E., Rodríguez, A., Basañez, L. (2007). Force Reflecting Teleoperation Via IPv6 Protocol with Geometric Constraints Haptic Guidance. In: Ferre, M., Buss, M., Aracil, R., Melchiorri, C., Balaguer, C. (eds) Advances in Telerobotics. Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, vol 31. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71364-7_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71364-7_27
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-71363-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-71364-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)