Abstract
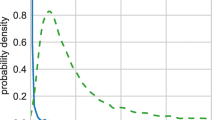
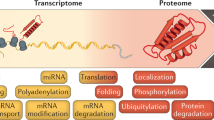
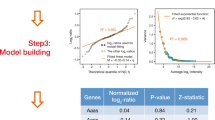
An important problem in biology is to understand correspondences between mRNA microarray levels and mass spectrometry peptide counts. Recently, a compendium of mRNA expression levels and protein abundances were released for the entire genome of the laboratory mouse, Mus musculus. The availability of these two data sets facilitate using machine learning methods to automatically infer plausible correspondences between the gene products. Knowing these correspondences can be helpful either for predicting protein abundances from microarray data or as an independent source of information that can be used for learning richer models such as regulatory networks. We propose a probabilistic model that relates protein abundances to mRNA expression levels. Using cross-mapped data from the above-mentioned studies, we learn the model and then score the genes for their strength of relationship by performing probabilistic inference in the learned model. While we gave a simplified outline of our technique in a publication aimed at biologists (Cell 2006), in this paper, we give a complete description of the Bayesian model and the computational technique used to perform inference. In addition, we demonstrate that the Bayesian technique achieves mappings with higher statistical significance, compared to standard linear regression and a maximum likelihood version of the proposed model.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kislinger, T., Cox, B., Kannan, A., et al.: Global survey of organ and organelle protein expression in mouse: combined proteomic and transcriptomic profiling. Cell 125(1), 173–186 (2006)
Greenbaum, D., Colangelo, C., Williams, K., Gerstein, M.: Comparing protein abundance and mRNA expression levels on a genomic scale. Genome Biol. 4(9), 117 (2003)
Gygi, S., Rochon, Y., Franza, B., Aebersold, R.: Correlation between protein and mRNA abundance in yeast. Mol. Cell Biology 19(3), 1720–1730 (1999)
Griffin, T., Gygi, S., Ideker, T., Rist, B., Eng, J., Hood, L., Aebersold, R.: Complementary profiling of gene expression at the transcriptome and proteome levels in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell Proteomics 1(4), 323–333 (2002)
Lian, Z., Kluger, Y., Greenbaum, D., Tuck, D., Gerstein, M., Berliner, N., Weissman, S., Newburger, P.: Genomic and proteomic analysis of the myeloid differentiation program: global analysis of gene expression during induced differentiation in the MPRO cell line. Blood 100(9), 3209–3220 (2002)
Mootha, V., Bunkenborg, J., Olsen, J., Hjerrild, M., Wisniewski, J., Stahl, E., Bolouri, M., Ray, H., Sihag, S., Kamal, M., Patterson, N., Lander, E., Mann, M.: Integrated analysis of protein composition, tissue diversity, and gene regulation in mouse mitochondria. Cell 115(5), 629–640 (2003)
Liu, H., Sadygov, R., Yates, J.: Model for Random Sampling and Estimation of Relative Protein Abundance in Shotgun Proteomics. Anal. Chem. 76(14), 4193–4201 (2004)
Zhang, W., Morris, Q., et al.: The functional landscape of mouse gene expression. Journal of Biology 3(5), 21 (2004)
Su, A., Wiltshire, T., Batalov, S., et al.: A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. PNAS 101(16), 6062–6067 (2004)
Duda, R., Hart, P.: Pattern Classification and Scene Analysis. Wiley-Interscience, Chichester (2000)
Jordan, M., Ghahramani, Z., Jaakkola, T., Saul, L.K.: An Introduction to Variational Methods for Graphical Models. in Machine Learning, 37-2 (1999)
Neal, R.M.: Probabilistic Inference Using Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Technical Report, University of Toronto, CRG-TR-93-1 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kannan, A., Emili, A., Frey, B.J. (2007). A Bayesian Model That Links Microarray mRNA Measurements to Mass Spectrometry Protein Measurements. In: Speed, T., Huang, H. (eds) Research in Computational Molecular Biology. RECOMB 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 4453. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71681-5_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71681-5_23
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-71680-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-71681-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)