Abstract
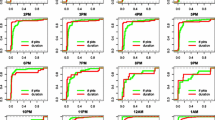
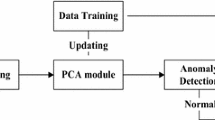
Third generation (3G) mobile networks rely on distributed architectures where Operation and Maintenance Centers handle a large amount of information about network behavior. Such data can be processed to extract higher-level knowledge, useful for network management and optimization. In this paper we apply reduction techniques, such as Principal Component Analysis, to identify orthogonal subspaces representing the more interesting data contributing to overall variance and to split them up in “normal” and “anomalous” subspaces. Patterns within anomalous subspaces allow for early detection of network anomalies, improving mobile networks management and reducing the risk of malfunctioning.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crovella, M., Bestavros, A.: Self-similarity in world wide web traffic: Evidence and possible causes. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw 5(6), 835–846 (1997)
Crovella, M.E., Kolaczyk, E.D.: Graph wavelets for spatial traffic analysis. In: IEEE Infocom, San Francisco, California, April 2003, IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (2003)
Deligiannakis, A., Kotidis, Y., Roussopoulos, N.: Compressing historical information in sensor networks. Paris, France (June 2004)
Geladi, P.: Analysis of multiway (multi-mode) data. Chem. Intell. Lab. 7, 11–30 (1989)
He, N., Zhang, J., Wang, S.: Combination of independent component analysis and multi-way principal component analysis for batch process monitoring. In: IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, October 2004, vol. 1, pp. 530–535 (2004)
Lakhina, A., Papagiannaki, K., Crovella, M.E., Diot, C., Kolaczyk, E.D., Taft, N.: Structural analysis of network traffic flows. In: Proc. of ACM SIGMETRICS, New York, NY, June 2004, ACM Press, New York (2004)
Esbensen, K., Wold, S., Geladi, P., Ohman, J.: Multiway principal components and pls-analysis. Journal Chemometr. 1, 41–56 (1987)
Shental, N., Hertz, T., Weinshall, D., Pavel, M.: Adjustment Learning and Relevant Component Analysis. In: Heyden, A., Sparr, G., Nielsen, M., Johansen, P. (eds.) ECCV 2002. LNCS, vol. 2353, pp. 776–790. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Yue, H.H., Nauert, C., Qin, S.J., Markle, R.J., Gatto, M.: Fault detection of plasma etchers using optical emission spectra. IEEE transaction on semiconductor manufactoring 13 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Anisetti, M., Ardagna, C.A., Bellandi, V., Bernardoni, E., Damiani, E., Reale, S. (2007). Anomalies Detection in Mobile Network Management Data. In: Kotagiri, R., Krishna, P.R., Mohania, M., Nantajeewarawat, E. (eds) Advances in Databases: Concepts, Systems and Applications. DASFAA 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4443. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71703-4_83
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71703-4_83
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-71702-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-71703-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)