Abstract
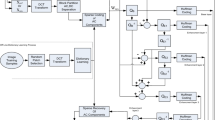
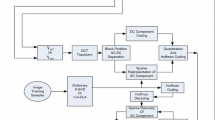
In this paper, a new residual signal compression method is proposed based on the blind signal decomposition for video coding. Blind signal decomposition is derived based on the fact that most of the natural signals in the real world could be decomposed into their basis signals and their weight values used in the composition process. In the proposed video coding system, composite data generated by adding two or more blocks are coded. Then the proposed decoder parses the coded bitstream and reconstructs the composite residual. The reconstructed composite residual is decomposed into the original residual blocks based on the blind signal decomposition. In the proposed system, the blind source separation is selectively used, depending on the performance of source separation. It is found that we can achieve approximately 2~3dB gain by embedding our algorithm into an MPEG-4 baseline encoder.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiegand, T., et al.: Overview of the H.264 / AVC Video Coding Standard. IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 560-576 (2003)
Overview of the MPEG-4 Standard, MPEG-4 Overview. ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11 14496-10 N4668 (2002)
Coding of Moving Picture and Audio, Draft of Version 4. ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11 14496-10 (E) N7081 (2005)
Amari, S., Cichocki, A., Yang, H.H.: A New Learning Algorithm for Blind Signal Separation. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 8, 757–763 (1996)
Bach, F.R., Jordan, M.I.: Kernel Independent Component Analysis. J. Machine Learning Res. 3, 1–48 (2002)
Lee, T.W., Girolami, M., Sejnowski, T.J.: Independent Component Analysis using an Extended Infomax Algorithm for Mixed Sub-Gaussian and Super-Gaussian Sources. Neural Comput. 11, 417–441 (1999)
Hyvarinen, A., Oja, E.: A Fast Fixed-Point Algorithm for Independent Component Analysis. Neural computation 9, 1483–1492 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Park, SN. et al. (2007). Residual Signal Compression Based on the Blind Signal Decomposition for Video Coding. In: Stajano, F., Kim, H.J., Chae, JS., Kim, SD. (eds) Ubiquitous Convergence Technology. ICUCT 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4412. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71789-8_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71789-8_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-71788-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-71789-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)