Abstract
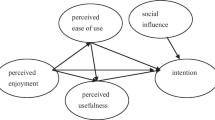
The purpose and characteristics of e-learning are different from other Web applications. This paper uses an extended Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) to explain the motivation, attitude and acceptance behind participants of e-learning. The factors that determine Web quality include the external variables: system functionality, interface design, pedagogic and contents, as well as community.. Perceived enjoyment was also added to this model as a factor. . The empirical results indicated that the extended TAM explains the acceptability of on-line learning systems with high reliability, validity, and model fitness. All “beliefs” (user perceptions)– perceived usefulness, ease of use, and enjoyment– are good predictors of attitude and acceptance. Pedagogic, and content as well as community are important external factors that predict e-learning acceptance.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagozzi, R.P., Yi, Y.: On the Evaluation of Structural Equation Models. Journal of Academy of Marketing Science 16(1), 74–94 (1988)
Barnes, S.J., Vidgen, R.T.: Measuring Web Site Quality Improvements: a Case Study of the Forum on Strategic Management Knowledge Exchange. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 297–309 (2003)
Bentler, P.M.: EQS Structural Equations Program Manual. Multivariate Software Inc., Encino (1995)
Cox, J., Dale, B.G.: Key Quality Factors in Web Site Design and Use: an Examination. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management 19, 862–888 (2002)
Davis, F.D., Bagozzi, R.P., Warshaw, P.R.: User Acceptance of Computer Technology: A Comparison of Two Theoretical Models. Management Science 35(8) (2002)
Davis, F.D.: Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Quarterly 13(3), 319–339 (1989)
Heijden, H.: Factors Influencing the Usage of Websites: the Case of a Generic Portal in The Netherlands. Information & Management 40, 541–549 (2003)
Hu, L., Bentler, P.M.: Cutoff Criteria for Fit Indexes in Covariance. Structural Equation Modeling 6(1), 1–55 (1999)
Jiang, J.J., Klein, G.C., Christopher, L.: Measuring Information System Service Quality: SERVQUAL from the Other Side. MIS Quarterly 26(2), 145–166 (2002)
Johnson, R.A., Hignite, M.A.: Applying the Technology Acceptance Model to the WWW. Academy of Information and Management Sciences Journal 3(2), 130–142 (2000)
Kim, S.-E., Shaw, T., Schneider, H.: Web Site Design Benchmarking within Industry Groups. Internet Research 13(1), 17–26 (2003)
Lin, C.-C., Lu, H.: Towards an Understanding of the Behavioural Intention to Use a Web Site. International Journal of Information Management 20, 197–208 (2000)
Meuter, M.L., Ostrom, A.L., Roundtree, R.I., Binter, M.J.: Self-service Technologies: Understanding Customer Satisfaction with Technology-based Service Encounters. Journal of Marketing 64(3), 50–64 (2000)
Moon, J.-W., Kim, Y.-G.: Extending the TAM for a World-Wide-Web context. Information & Management 38, 217–230 (2001)
Mulaik, S.A., James, L.R., Van Altine, J., Bennett, N., Lind, S., Stilwell, C.D.: Evaluation of Goodness-of-fit Indices for Structural Equation Models. Psychological Bulletin 105, 430–445 (1989)
McDonald, R.P., Ho, M.R.: Principles and Practice in Reporting Structural Equation Analysis. Psychological Methods 7, 64–82 (2002)
Parasuraman, A., Zeitham, V.A., Berry, L.L.: Service Quality: A Multiple-item Scale for Measuring Consumer Perceptions of Service Quality. Journal of Retailing 64(1) (1988)
Prensky, M.: Digital game-based learning. McGraw-Hill, New York (2001)
Swan, K.: Relationships between Interactions and Learning in Online Environments (2004), Available: http://www.sloan-c.org/publications/books/interactions.pdf
Landry, B.J., Griffeth, R., Hartman, S.: Measuring Student Perceptions of Blackboard Using the Technology Acceptance Model. Decision Science Journal of Innovative Education 4(1) (2006)
Kiili, K.: Digital games-based learning: Towards an experiential gaming model. The Internet and Higher Education 8(3), 13–24 (2005)
Chao, T., Saj, T., Tessier, F.: Establishing a Quality Review for Online Courses. EDUCAUSE Quarterly 3 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fu, FL., Chou, HG., Yu, SC. (2007). Activate Interaction Relationships Between Students Acceptance Behavior and E-Learning. In: Dong, G., Lin, X., Wang, W., Yang, Y., Yu, J.X. (eds) Advances in Data and Web Management. APWeb WAIM 2007 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4505. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72524-4_69
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72524-4_69
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-72483-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-72524-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)