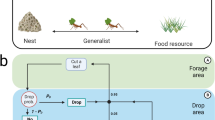
Division of labour is one of the possible strategies to efficiently exploit the resources of autonomous systems. It is also a phenomenon often observed in animal systems. We show an architecture that implements division of labour in Sensor/Actuator Networks. The way the nodes take their decisions is inspired by ants’ foraging behaviour. The preliminary results show that the architecture and the bio-inspired mechanism successfully induce self-organised division of labour in the network. The experiments were run in simulation. We developed a new type of simulator for this purpose. Key features of our work are cross-layer design and exploitation of inter-node interactions. No explicit negotiation between the agents takes place.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I., Kasimoglu, I.: Wireless sensor and actor networks: research challenges. Ad Hoc Networks 2 (2004) 351-367
Cardei, M., Wu, J.: Coverage in Wireless Sensor Networks. In Ilyas, M., ed.: Handbook of Sensor Networks. CRC Press, West Palm Beach, FL (2004)
Labella, T., Dorigo, M., Deneubourg, J.L.: Division of labor in a group of robots inspired by ants’ foraging behavior. ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive Systems 1 (2006)4-25
Labella, T., Dorigo, M., Deneubourg, J.L.: Efficiency and task allocation in prey retrieval. In Ijspeert, A., Murata, M., Wakamiya, N., eds.: Biologically Inspired Approaches to Advanced Information Technology: First International Workshop, BioADIT 2004. Volume 3141 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science., Springer Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany (2004)
Dressler, F.: Self-Organization in Ad Hoc Networks: Overview and Classification. Technical Report 02/06, University of Erlangen, Dept. of Computer Science 7 (2006)
Gerkey, B., Matarić , M.: A market-based formulation of sensor-actuator network coordination. In Sukhatme, G., Balch, T., eds.: Proceedings fo the AAAI Sping Symposium on Intelligent Embedded and Distributed Systems, AAAI Press, San Jose, CA (2002) 21-26
Younis, M., Akkaya, K., Kunjithapatham, A.: Optimization of Task Allocation in a Cluster-Based Sensor Network. In: Proceedings of the Eighth IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC 2003), IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, CA (2003)329-334
Batalin, M., Sukhatme, G.: Using a sensor network for distributed multi-robot task allocation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA2004). Volume 1., IEEE Press, New York, NY (2004) 158-164
Low, K., Leow, W., Ang, M.: Autonomic mobile sensor network with self-coordinated task allocation and execution. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part C 36 (2006) 315-327
Bonabeau, E., Theraulaz, G., Deneubourg, J.L.: Quantitative study of the fixed threshold model for the regulation of division of labor in insect societies. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B-Biological Sciences 263 (1996) 1565-1569
Jesi, G., Montresor, A., Babaoglu, O.: Proximity-aware superpeer overlay technologies. In Keller, A., Martin-Flatin, J.P., eds.: Proceedings of SelfMan’06. Volume 3996 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science., Springer Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany (2006) 43-57
Labella, T., Dietrich, I., Dressler, F.: BARAKA: A hybrid simulator of sensor/actuator networks. In: Proceedings of the Second IEEE/Create-Net/ICST International Conference on COMmunication System softWAre and MiddlewaRE (COMSWARE 2007), Bangalore, India (2007)
Jakobi, N., Husbands, P., Harvey, I.: Noise and the reality gap: the use of simulation in evolutionary robotics. In Moran, F., Moreno, A., Merelo, J., Chacon, P., eds.: Advances in Artificial Life: Proceedings of the Third European Conference on Artificial Life. Volume 929 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science., Springer Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany (1995)704-720
Bonabeau, E., Dorigo, M., Theraulaz, G.: Swarm Intelligence: From Natural to Artificial Systems. Oxford University Press, New York (1999)
Abolhasan, M., Wysocki, T., Dutkiewicz, E.: A review of routing protocols for mobile adhoc networks. Ad Hoc Networks 2 (2004) 1-22
Di Caro, G., Ducatelle, F., Gambardella, L.: AntHocNet: An adaptive nature-inspired algorithm for routing in mobile ad hoc networks. European Transactions on Telecommunications, Special Issue on Self-organization in Mobile Networking 16 (2005) 443-455
Perkins, C., Royer, E.: Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Routing. In: 2nd IEEE Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, CA (1999) 90-100
Balch, T.: Hierarchic social entropy: An information theoretic measure of robot group diversity. Autonomous Robots 8 (2000) 209-238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Labella, T.H., Dressler, F. (2007). A Bio-Inspired Architecture for Division of Labour in SANETs. In: Dressler, F., Carreras, I. (eds) Advances in Biologically Inspired Information Systems. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 69. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72693-7_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72693-7_11
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-72692-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-72693-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)