Abstract
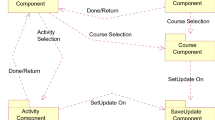
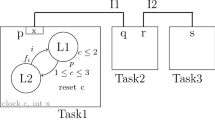
Communication delay is a main obstacle in global cooperative software design and rescheduling design tasks is essential to reduce such a impact. The duration of task and communication delay is undetermined in global software design, and the task sequence is not determined when rework is required to fix the possible defects in the progress. Therefore, it is hard to distinguish when and which task should be handled and the design task rescheduling can be difficult to accomplish. Dynamic Micro-estimation refines the estimation of effort and duration for the tasks in the next short period. Based on Multiple Component Status Transition Graph (MCSTG) and Micro-estimation, the probability of a task should be handled and the available time for this task to be finished can be easily estimated. The Micro-estimation extended MCSTG enables the project managers to reschedule the tasks according to their criticality and importance so as to facilitate the collaboration in global software design.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herbsleb, J.D., Mockus, A.: An Empirical Study of Speed and Communication in Globally Distributed Software Development. IEEE Trans. on Software Engi. 29(6), 481–492 (2003)
Herbsleb, J.D., Moitra, D.: Global Software Development. IEEE Software 18(2), 16–20 (2001)
Carmel, E.: Global Software Teams: Collaborating, Across Borders and Time Zones. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River (1999)
Carmel, E., Agarwal, R.: Tactical Approaches for Alleviating Distance in Global Software Development. IEEE Software 18(2), 22–29 (2001)
Olson, J.S., Teasley, S.: Groupware in the Wild: Lessons Learned from a Year of Virtual Collocation. In: Proc. ACM 1996 Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative work, pp. 419–427 (1996)
Karolak, D.W.: Global Software Development. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (1998)
Mockus, A., Weiss, D.M.: Globalization by Chunking: A Quantitative Approach. IEEE Software 18(2), 30–37 (2001)
Xu, B., et al.: Global Cooperative Design in Legacy System Reengineering Project. In: Proc. 8th CSCWD Conference, Xiamen, China, pp. 483–486 (2004)
Allen, T.J.: Managing the Flow of Technology. MIT Press, Cambridge (1977)
Grinter, R.E., Herbsleb, J.D., Perry, D.E.: The Geography of Coordination: Dealing with Distance in R&D Work. In: Proc. Int’l ACM SIGROUP Conf. Supporting Group Work, pp. 306–315 (1999)
Xu, B., et al.: Enhancing Coordination in Global Cooperative Software Design. In: Proc. 9th CSCWD Conference, Coventry, UK, pp. 22–26 (2005)
Yang, X., Xu, B.: Towards Adaptive Tasks Arrangement in Offshore Outsourcing Software Development. In: Yeung, D.S., et al. (eds.) ICMLC 2005. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3930, pp. 654–657. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, B., Hu, H., Ling, Y., Yang, X., He, Z., Ma, A. (2007). Achieving Better Collaboration in Global Software Design with Micro Estimation. In: Shen, W., Luo, J., Lin, Z., Barthès, JP.A., Hao, Q. (eds) Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design III. CSCWD 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4402. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72863-4_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72863-4_37
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-72862-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-72863-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)