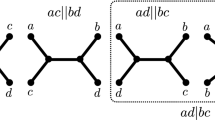
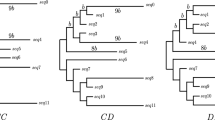
Abstract
In this paper we introduce a new quartet-based method for phylogenetic inference. This method concentrates on reconstructing reliable phylogenetic trees while tolerating as many quartet errors as possible. This is achieved by carefully selecting two possible neighbor leaves to merge and assigning weights intelligently to the quartets that contain newly merged leaves. Theoretically we prove that this method will always reconstruct the correct tree when a completely consistent quartet set is given. Intensive computer simulations show that our approach outperforms widely used quartet-based program TREE-PUZZLE in most of cases. Under the circumstance of low quartet accuracy, our method still can outperform distance-based method such as Neighbor-joining. Experiments on the real data set also shows the potential of this method. We also propose a simple technique to improve the quality of quartet set. Using this technique we can improve the results of our method.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi, J., Hasegawa, M.: Instability of quartet analyses of molecular sequence data by the maximum likelihood method: the cetacean/artiodactyla relashionships Cladistics 5, 164–166 (1999)
Felsenstein, J.: Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 17, 368–376 (1981)
Li, M., Chen, X., Li, X., Ma, B., Paul, M.B.: The Similarity Metric. IEEE Transections On Information Theory 50(12) (2004)
Rambaut, A., Grassly, N.C.: Seq-Gen: An application for the Monte Carlo simulation of DNA sequence evolution along phylogenetic trees. Comput. Appl. Biosci. (1996)
Ranwez, V., Gascuel, O.: Quartet-Based Phylogenetic Inference:Improvement and Limits. Mol. Biol. Evol. 18(6), 1103–1116 (2001)
Reyes, A., Gissi, C., Pesole, G., Catzeflis, F.M., Saccone, C.: Where Do Rodents Fit? Evidence from the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Sciurus vulgaris. Molecular Biology and Evolution 17, 979–983 (2000)
Robinson, D.F., Foulds, L.R.: Comparison of phylogenetic trees. Math. Biosci. 53, 131–147 (1981)
Saitou, N., Nei, M.: The Neighbor-joining Method: A New Method for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees. Mol. Bio. Evol. 4(4), 406–425 (1987)
Strimmer, K., Goldman, N., Von Haeseler, A.: Quartet puzzling:a quartet maximum-likeihood method for reconstructing tree topologies. Mol. biol. E 13, 964–969 (1996)
Strimmer, K., Goldman, N., Von Haeseler, A.: Bayesian probabilities and quartet puzzling. Mol. biol. E 14, 210–211 (1997)
Schmidt, H.A., Strimmer, K., Vingron, M.: TREE-PUZZLE: maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics 18(3), 502–504 (2002)
Zhou, B.B., Tarawneh, M., Wang, C.: A Novel Quartet-based Method for Phylogenetic Inference. In: Proceedings of 5th IEEE Symposium on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering 2005, IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xin, L., Ma, B., Zhang, K. (2007). A New Quartet Approach for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees: Quartet Joining Method. In: Lin, G. (eds) Computing and Combinatorics. COCOON 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4598. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73545-8_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73545-8_7
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-73544-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-73545-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)