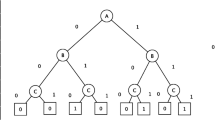
Abstract
In context-aware system, applications should adjust their execution policies in the light of context information of equipment, such as equipment’s position, electric power, network bandwidth, and so on. In various context-aware systems, an important solution is to isolate executable codes in different context into a number of program segments and to select different execution policies according to the context in the process of operation, thus increasing the programming flexibility. Since not all possible contexts can be taken into consideration in the definition of policies, several policies might meet the current context simultaneously in some given environments, thus resulting in policy conflict. This paper proposes a kind of conflict solution algorithm, which, through defining the context center of each execution policy, computes the offset between the current context and the center and selects the one closest to the current context as the execution policy in the case of conflict. Experiments testify that the algorithm can effectively eliminate conflicts of policy selection and well manifest the intention of policy definition, making policy selection more reasonable.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Want, R., Hopper, A., Falcao, V., Gibbons, J.: The active badge location system. ACM Transactions on Information Systems 10(1), 91–102 (1992)
Salber, D., Dey, A.K., Abowd, G.: The context toolkit: Aiding the development of context-enabled applications. In: ACM SIGCHI Conf. Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 99), New York, pp. 434–441. ACM Press, New York (1999)
Romn, M., Hess, C.K., Cerqueira, R., Ranganathan, A., Campbell, R.H., Nahrstedt, K.: Gaia: A middleware infrastructure to enable active spaces. IEEE Pervasive Computing, 74–83 (2002)
Keays, R., Rakotonirainy, A.: Context-oriented programming. In: MobiDe 2003. Proceedings of the 3rd ACM international workshop on Data engineering for wireless and mobile access, New York, NY, USA, pp. 9–16. ACM Press, New York (2003)
Ranganathan, A., Chetan, S., Al-Muhtadi, J., Campbell, R.H., Mickunas, M.D.: Olympus: A high-level programming model for pervasive computing environments. In: Third IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, 2005. PerCom 2005, pp. 7–16. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (2005)
Mascolo, L.C., Emmerich, W., Cecilia: Carisma: Context-aware reflective middleware system for mobile applications. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering 29, 929–944 (2003)
Nishigaki, K., Yasumoto, K., Shibata, N., Ito, M., Higashino, T.: Framework and rule-based language for facilitating context-aware computing using information appliances. In: Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Services and Infrastructure for the Ubiquitous and Mobile Internet (SIUMI) (ICDCSW 2005), vol. 3, pp. 345–351 (2005)
Pirjanian, P.: Behavior coordination mechanisms – state-of-the-art. Technical Report IRIS-99-375, Institute of Robotics and Intelligent Systems, School of Engineering, University of Southern California (October 1999)
Ranganathan, A., Campbell, R.H.: An infrastructure for context-awareness based on first order logic. Journal of Personal and Ubiquitous Computing 7(6), 353–364 (2003)
Hanssens, N., Kulkarni, A., Tuchinda, R., Horton, T.: Building agent-based intelligent workspaces. In: Proceedings of ABA Conference (2002)
Keeney, J.: Chisel: A policy-driven, context-aware, dynamic adaptation framework. In: POLICY 2003. Proceedings of the Fourth IEEE International Workshop on Policies for Distributed Systems and Networks, pp. 3–14. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (2003)
Minkyoung, K., Hyun, K.: Behavior coordination mechanism for intelligent home. In: ICIS-COMSAR 2006, pp. 452–457 (2006)
Preuveneers, D., Berbers, Y.: Multi-dimensional dependency and conflict resolution for self-adaptable context-aware systems. In: International Conference on Autonomic and Autonomous Systems, 2006. ICAS 2006, p. 36 (2006)
Insuk, P., Lee, D., Hyun, S.J.: A dynamic context-conflict management scheme for group-aware ubiquitous computing environments. In: 29th Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference, 2005. COMPSAC 2005, vol. 1, pp. 359–364 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xi, M., Zhao, J., Qi, Y., He, H., Liu, L. (2007). An Offset Algorithm for Conflict Resolution in Context-Aware Computing. In: Indulska, J., Ma, J., Yang, L.T., Ungerer, T., Cao, J. (eds) Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing. UIC 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4611. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73549-6_86
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73549-6_86
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-73548-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-73549-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)