Abstract
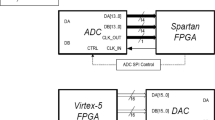
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is the most basic and essential operation performed in Software Defined Radio (SDR). Thus designing regular, reconfigurable, modular, low hardware and timing-complexity FFT computation block is very important. A single FFT block should be configurable for varying length FFT computation and also for computation of different transforms like Discrete cosine/sine transform (DCT/DST) etc. In this paper, the authors analyze area, timing complexity and noise to signal Ratio (NSR) of Bruun’s FFT w.r.t. classical FFT from a SDR perspective. It is shown that architecture of Bruun’s FFT is ideally suited for SDR and may be used in preference over classical FFT for most practical cases. A detailed comparison of Bruun’s and classical FFT hardware architectures for same NSR is carried out and results of FPGA implementation are discussed.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitola, J.: The Software Radio Architecture. IEEE Communications Magazine, 26–38 (May 1995)
Tuttlebee, W.: Evolution of radio systems into the 21st century. In: Proc. IEE Int. conf. on Radio receivers an associated systems (1995)
Reed, J.H.: Software Radio: A Modern Approach to Radio Engineering. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2000)
Lin, Y.T., Tsai, P.Y., Chiueh, T.D.: Low-power variable-length fast Fourier transform processor. In: IEE Proceedings-Computers and Digital Techniques (July 2005)
Hung, C.-P., Chen, S.-G., Chen, K.-L.: Design of an efficient variable-length FFT processor. In: International Symposium on Circuits and Systems(ISCAS) (2004)
Britanak, V., Rao, K.R.: Two-Dimensional DCT/DST Universal Computational Structure for 2m X 2n Block Sizes. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing 48(11), 3250–3255 (2000)
Tell, E., Seger, O., Liu, D.: A converged hardware solution for FFT, DCT and Walsh transform. In: Seventh International symposium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, pp. 609–612 (2003)
Bruun, G.: Z-Transform DFT filters and FFT’s. IEEE Trans.Acoust. Speech, Signal Processing ASSP-26, 56–63 (1978)
Storn, R.: Some Results in Fixed Point Error Analysis of the Bruun-FFT Algorithm. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing. 41(7) (1993)
Oppenheim, A.V., Schafer, R.: Digital Signal Processing.Pearson Education (2004)
Parhami, B.: Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardwrae Designs. Oxford University Press, New York (2000)
Zimmermann, R.: Binary Adder Architectures for Cell-Based VLSI and their Synthesis, PhD thesis, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich, Hartung-Gorre Verlag (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mittal, S., Khan, M.Z.A., Srinivas, M.B. (2007). A Comparative Study of Different FFT Architectures for Software Defined Radio. In: Vassiliadis, S., Bereković, M., Hämäläinen, T.D. (eds) Embedded Computer Systems: Architectures, Modeling, and Simulation. SAMOS 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4599. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73625-7_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73625-7_39
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-73622-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-73625-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)