Abstract
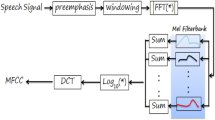
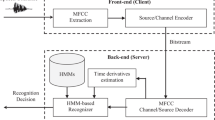
Traditional speech recognition systems have relied on power spectral densities, Mel-frequency cepstral, linear prediction coding and formant analysis. This paper introduces two novel input feature sets and their extraction methods for intelligent phoneme identification. These input sets are based on intrinsic phonetic characteristics of Arabic speech comprising of the dimensionally reduced Power Spectral Densities (DPSD) and Location, Trend, Gradient (LTG) values of the captured speech signal spectrum. These characteristics have been subsequently utilized as inputs to four different neural network based recognition classifiers. The classifiers have been tested for twenty-eight Arabic phonemes utterances from over one hundred non-native speakers. The results obtained using the proposed feature sets have been compared and it has been observed that LTG based input feature set provides an average phoneme identification accuracy of 86% as compared to 70% obtained through applying DPSD based inputs for similar classifiers. It is worthwhile to note that the methods proposed in this paper are generic and are equally applicable to other regional languages such as Persian and Urdu.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirchhoff, K.: Novel Speech Recognition Models for Arabic, Johns-Hopkins University, Technical Report (2002) http://www.clsp.jhu.edu/ws2002/groups/arabic/ available on April 28, 2005
Kohonen, T.: Physiological Interpretation of the Self Organizing Map Algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 6, 895–905 (1993)
Kohonen, T.: New Developments and Applications of Self-Organizing Maps. In: NICROSP. Proceedings of International Workshop on Neural Networks for Identification, Control, Robotics, and Signal/Image Processing, Venice, pp. 164–172. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (1996)
Specht, D.F.: A general regression neural network. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 2(6), 568–576 (1991)
Neagoe, V.E., Ropot, A.D.: Concurrent Self-Organizing Maps for Pattern Classification. In: IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Informatics, pp. 304-312 (2002)
Somervuo, P.: Self-Organizing Maps for Signal and Symbol Sequences, PhD Thesis Helsinki University of Technology, Neural Networks Research Centre (2000)
Díaz, F., Ferrández, J.M., Gómez, P., Rodellar, V., Nieto, V.: Spoken-Digit Recognition using Self-organizing Maps with Perceptual Pre-processing. In: IWANN’97, International Work-Conference on Artificial and Natural Neural Networks, Spain, pp. 1203-1212 (1997)
Samouelian, A.: Knowledge Based Approach to Consonant Recognition. In: ICASSP ’94. Proceedings of International Conference on Acoustic Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 77–80 (1994)
Wooters, C., Stolcke, A.: Multiple-Pronunciation Lexical Modeling in A Speaker Independent Speech Understanding System. In: ICSLP ’94. Proceedings of International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, pp. 453–456 (1994)
Astrid, H., Andrew, M.: Recent Advances in the Multi-stream HMM/ANN Hybrid Approach to Noise Robust ASR. Computer Speech & Language 19(1), 3–30 (2005)
Yuk, D., Flanagan, J.: Telephone Speech Recognition using Neural Networks and Hidden Markov Models. In: ICASSP ’99, Proceedings of International Conference on Acoustic Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 157–160 (1999)
Wong, E., Sridharan, S.: Comparison of Linear Prediction Cepstrum Coefficients and Mel-Frequency Cepstrum Coefficients for Language Identification. In: International Symposium on Intelligent Multimedia, Video and Speech Processing, Hong Kong, pp. 95–98 (2001)
He, J.L., Liu, L., Palm, G.: On the Use of Residual Cepstrum in Speech Recognition. In: ICASSP’96. IEEE Proceedings of International Conference on Acoustic Speech and Signal Processing, vol.1, Atlanta, USA, pp. 5-8 (1996)
Rudzionis, A., Rudzionis, V.: Phoneme Recognition in Fixed Context Using Regularized Discriminant Analysis. In: Proceedings of 6th European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology, Eurospeech’99, Budapest, Hungary, pp. 2745–2748 (1999)
Campbell, W.M., Campbell, J.P., Reynolds, D.A., Singer, E., Torres-Carrasquillo, P.A.: Support Vector Machines for Speaker and Language Recognition. Computer Speech & Language 20(2-3), 210–229 (2006)
Gales, M.J.F., Airey, S.S.: Product of Gaussians for Speech Recognition. Computer Speech & Language 20(1), 22–40 (2006)
Yousif, A.E.: Phonetization of Arabic: Rules and Algorithms. Computer Speech & Language 18(4), 339–373 (2004)
Wiki_Arabic: http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Arabic/ Arabic_sounds
Yousef, A.A.: High Performance Arabic Digits Recognizer Using Neural Networks. In: The 2003 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks-IJCNN2003, Portland, Oregon (2003)
Yousef, A.A.: Analyzing Arabic Digit Recognizer Errors Using Spectrograms. In: ICSP ’04. Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Signal Processing, pp. 646-650 (2004)
Debyeche, H.M.: A Knowledge-based Approach for Arabic Amphatic Consonant Identification Based on Speech Spectrogram Reading. In: Proceedings of the Thirtieth Southeastern Symposium on System Theory, pp. 325 – 328 (1998)
Jalaleddin, A., Egidio, M.: The Status of Vowels in Jordanian and Moroccan Arabic: Insights from Production and Perception. The Journal of the Acous. Soc. of America (2004)
Mohamed, A., Ratree, W.: Acoustic Characteristics of Fricatives in Arabic. The Journal of the Acous. Soc. of America, 2655-2689 (2001)
Zue, V.W., Lamel, L.F.: An Expert Spectrogram Reader: A Knowledge-Based Approach to Speech Recognition. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Acoustic Speech and Signal Processing ICASSP ’86, Japan, pp. 1197-1200 (April 1986)
Ingle, V.K., Proakis, J.G.: Digital Signal Processing Using MATLAB, Thomson Engineering (1999)
Press, W.H., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling, W.T., Flannery, B.P.: Numerical Recipes in C: the Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1992)
McCandless, S.: An Agorithm for Automatic Formant Extraction Using Linear Prediction Spectra. IEEE Transactions of Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing ASSP-22(2), 135–141 (1974)
Rabiner, L., Juang, B.: Fundamentals of Speech Recognition. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey (1993)
Awais, M.M., Masud, S., Shamail, S., Akhtar, J.: A Hybrid Multi-Layered Speaker Independent Arabic Phoneme Identification System. In: Yang, Z.R., Yin, H., Everson, R.M. (eds.) IDEAL 2004. LNCS, vol. 3177, pp. 23–25. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Awais, M.M., Masud, S., Ahktar, J., Shamail, S. (2007). Arabic Phoneme Identification Using Conventional and Concurrent Neural Networks in Non Native Speakers. In: Huang, DS., Heutte, L., Loog, M. (eds) Advanced Intelligent Computing Theories and Applications. With Aspects of Theoretical and Methodological Issues. ICIC 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4681. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74171-8_90
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74171-8_90
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-74170-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-74171-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)