Abstract
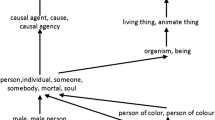
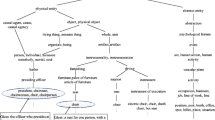
A major lack in the existing semantic similarity methods is that no one takes into account the context or the considered domain. However, two concepts similar in one context may appear completely unrelated in another context. In this paper, our first-level approach is context-dependent. We present a new method that computes semantic similarity in taxonomies by considering the context pattern of the text corpus. In addition, since taxonomies and corpora are interesting resources and each one has its strengths and weaknesses, we propose to combine similarity methods in our second-level multi-source approach. The performed experiments showed that our approach outperforms all the existing approaches.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
And, N.S.: An intrinsic information content metric for semantic similarity in wordnet
Barsalou, L.: Intraconcept similarity and its application for interconcept similarity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1989)
Christopher, H.S.: MANNING. Foundations of statistical natural language processing (1999)
Church, K.W., Hanks, P.: Word association norms, mutual information, and lexicography. In: Proceedings of the 27th. Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, pp. 76–83. Association for Computational Linguistics (1989)
Dagan, I., Lee, L., Pereira, F.C.N.: Similarity-based models of word cooccurrence probabilities. Machine Learning 34(1-3), 43–69 (1999)
Furnas, G.W., Deerwester, S.C., Dumais, S.T., Landauer, T.K., Harshman, R.A., Streeter, L.A., Lochbaum, K.E.: Information retrieval using a singular value decomposition model of latent semantic structure. In: Chiaramella, Y. (ed.) SIGIR, pp. 465–480. ACM Press, New York (1988)
Hindle, D.: Noun classification from predicate-argument structures. In: Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 268–275 (1990)
Hirst, G., St-Onge, D.: Lexical chains as representation of context for the detection and correction malapropisms (1997)
Jiang, J.J., Conrath, D.W.: Semantic similarity based on corpus statistics and lexical taxonomy (1997)
Leacock, C., Chodorow, M., Miller, G.A.: Using corpus statistics and wordnet relations for sense identification. Computational Linguistics 24(1), 147–165 (1998)
Lin, D.: An information-theoretic definition of similarity. In: Proc. 15th International Conf. on Machine Learning, pp. 296–304. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (1998)
Medin, D.: Psychological essentialism. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1989)
Miller, G.A.: Wordnet: A lexical database for english. Commun. ACM 38(11), 39–41 (1995)
Miller, G.A., Charles, W.: Contextual correlated of semantic similarity. Language and Cognitive Processes 6, 1–28 (1991)
Rada, R., Mili, H., Bicknell, E., Blettner, M.: Development and application of a metric on semantic nets. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics 19(1), 17–30 (1989)
Resnik, P.: Semantic similarity in a taxonomy: An information-based measure and its application to problems of ambiguity in natural language. J. Artif. Intell. Res. (JAIR) 11, 95–130 (1999)
Turney, P.D.: Mining the Web for synonyms: PMI–IR versus LSA on TOEFL. In: Flach, P.A., De Raedt, L. (eds.) ECML 2001. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2167, p. 491. Springer, Heidelberg (2001)
Tversky, A.: Features of similarity. Psychological Review 84, 327–352 (1977)
Wu, Z., Palmer, M.: Verb semantics and lexical selection. In: 32nd. Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, New Mexico, pp. 133–138 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
El Sayed, A., Hacid, H., Zighed, D. (2007). A Multisource Context-Dependent Semantic Distance Between Concepts. In: Wagner, R., Revell, N., Pernul, G. (eds) Database and Expert Systems Applications. DEXA 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4653. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74469-6_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74469-6_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-74467-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-74469-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)