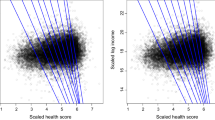
Abstract
In this paper we explore the use of Tree Augmented Naive Bayes (TAN) in regression problems where some of the independent variables are continuous and some others are discrete. The proposed solution is based on the approximation of the joint distribution by a Mixture of Truncated Exponentials (MTE). The construction of the TAN structure requires the use of the conditional mutual information, which cannot be analytically obtained for MTEs. In order to solve this problem, we introduce an unbiased estimator of the conditional mutual information, based on Monte Carlo estimation. We test the performance of the proposed model in a real life context, related to higher education management, where regression problems with discrete and continuous variables are common.
This work has been supported by the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science, project TIN2004-06204-C03-01 and by Junta de Andalucía, project P05-TIC-00276.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chow, C.K., Liu, C.N.: Approximating discrete probability distributions with dependence trees. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 14, 462–467 (1968)
Cobb, B., Rumí, R., Salmerón, A.: Modeling conditional distributions of continuous variables in Bayesian networks. In: Famili, A.F., Kok, J.N., Peña, J.M., Siebes, A., Feelders, A. (eds.) IDA 2005. LNCS, vol. 3646, pp. 36–45. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Cobb, B., Shenoy, P.P., Rumí, R.: Approximating probability density functions with mixtures of truncated exponentials. Statistics and Computing 16, 293–308 (2006)
Duda, R.O., Hart, P.E., Stork, D.G.: Pattern classification. Wiley Interscience, Chichester (2001)
Frank, E., Trigg, L., Holmes, G., Witten, I.H.: Technical note: Naive Bayes for regression. Machine Learning 41, 5–25 (2000)
Friedman, N., Geiger, D., Goldszmidt, M.: Bayesian network classifiers. Machine Learning 29, 131–163 (1997)
Gámez, J.A., Salmerón, A.: Predicción del valor genético en ovejas de raza manchega usando técnicas de aprendizaje automático. In: Actas de las VI Jornadas de Transferencia de Tecnología en Inteligencia Artificial, Paraninfo, pp. 71–80 (2005)
Jensen, F.V.: Bayesian networks and decision graphs. Springer, Heidelberg (2001)
Moral, S., Rumí, R., Salmerón, A.: Mixtures of truncated exponentials in hybrid Bayesian networks. In: Benferhat, S., Besnard, P. (eds.) ECSQARU 2001. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2143, pp. 135–143. Springer, Heidelberg (2001)
Moral, S., Rumí, R., Salmerón, A.: Approximating conditional MTE distributions by means of mixed trees. In: Nielsen, T.D., Zhang, N.L. (eds.) ECSQARU 2003. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2711, pp. 173–183. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Morales, M., Rodríguez, C., Salmerón, A.: Selective naive Bayes predictor using mixtures of truncated exponentials. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Mathematical and Statistical Modelling (ICMSM 2006) (2006)
Pearl, J.: Probabilistic reasoning in intelligent systems. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (1988)
Pérez, A., Larrañaga, P., Inza, I.: Supervised classification with conditional Gaussian networks: Increasing the structure complexity from naive Bayes. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 43, 1–25 (2006)
Quinlan, J.R.: Induction of decision trees. Machine Learning 1, 81–106 (1986)
Romero, V., Rumí, R., Salmerón, A.: Learning hybrid Bayesian networks using mixtures of truncated exponentials. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 42, 54–68 (2006)
Rumí, R., Salmerón, A.: Approximate probability propagation with mixtures of truncated exponentials. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning (in press, 2007)
Rumí, R., Salmerón, A., Moral, S.: Estimating mixtures of truncated exponentials in hybrid Bayesian networks. Test 15, 397–421 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fernández, A., Morales, M., Salmerón, A. (2007). Tree Augmented Naive Bayes for Regression Using Mixtures of Truncated Exponentials: Application to Higher Education Management. In: R. Berthold, M., Shawe-Taylor, J., Lavrač, N. (eds) Advances in Intelligent Data Analysis VII. IDA 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4723. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74825-0_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74825-0_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-74824-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-74825-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)