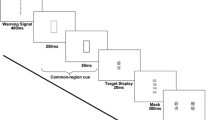
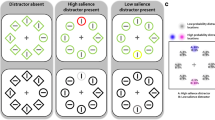
Abstract
Recently, a new fundamental discovery has been made of the relationship between attentional system and affective system of human brain, giving rise to the devaluation-by-inhibition hypothesis. It is shown that selective attention has an affective impact on an otherwise emotionally bland stimulus. Particularly, if a neutral stimulus was inhibited by selective attention in a prior task, it would be valued less in a subsequent affective evaluation task than it would otherwise have been. In the present study, we extend this line of research on the affective consequence of attention and demonstrate that prior attentional states (attended or inhibited) associated with a group of neutral stimuli (character strings) can even influence subsequent preference judgment about previously-unseen stimuli if these new stimuli share certain basic features (e.g., follow the same rule) with those encountered in a previous stage.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, A.K., Wais, P.E., Gabrieli, J.D.E.: Emotion Enhances Remembrance of Neutral Events Past. PNAS 103, 1599–1604 (2006)
Bechara, A.: The Role of Emotion in Decision-making: Evidence from Neurological Patients with Orbitofrontal Damage. Brain and Cognition 55, 30–40 (2004)
Bush, G., Luu, P., Posner, M.I.: Cognitive and Emotional Influences in Anterior Cingulate Cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 4, 215–222 (2000)
Cacioppo, J.T., Gardner, W.L.: Emotion. Annual Review of Psychology, pp. 191–192 (1999)
Dienes, Z., Altmann, G.T.M., Kwan, L., Goode, A.: Unconscious Knowledge of artificial grammars is applied strategically. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 21, 1322–1338 (1995)
Fenske, M.J., Raymond, J.E.: Affective Influences of Selective Attention. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 15, 312–316 (2006)
Fenske, M.J., Raymond, J.E., Kessler, K., Westoby, N., Tipper, S.P.: Research Report Attentional Inhibition Has Social-Emotional Consequences for Unfamiliar Faces. Psychological Science. 16, 753 (2005)
Hao, F., Zhang, H., Fu, X.: Modulation of Attention by Faces Expressing Emotion: Evidence from Visual Marking. In: Tao, J., Tan, T., Picard, R.W. (eds.) ACII 2005. LNCS, vol. 3784, Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Knowlton, B.J., Squire, L.R.: Artificial Grammar Learning Depends on Implicit Acquisition of Both Rule-based and exemplar-based information. Journal of Experimental Psychology. 1150, 169–181 (1996)
McCabe, S.B., Gotlib, I.H.: Selective Attention and Clinical Depression: Performance on a Deployment-of-attention Task. J Abnorm Psychol. 104, 241–245 (1995)
Raymond, J.E., Fenske, M.J., Westoby, N.: Emotional Devaluation of Distracting Patterns and Faces: A Consequence of Attentional Inhibition During Visual Search? Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 31, 1404–1415 (2005)
Reber, A.S.: Implicit learning of synthetic languages. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior. 6, 855–863 (1967)
Rowe, G., Hirsh, J.B., Anderson, A.K.: Positive Affect Increases the Breadth of Attentional selection. PNAS 104, 383–388 (2007)
Schneider, W., Eschman, A., Zuccolotto, A.: E-Prime User’s Guide: Psychology Software Tools (2002)
Stadler, M.A., Frensch, P.A.: Handbook of implicit learning: Sage Publications. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks, CA (1998)
Strongman, K.T.: The Psychology of Emotion: From Everyday Life to Theory, 5th edn. Wiley, Chichester (2003)
Tanaka, D., Kiyokawa, S., Yamada, A., Shigemasu, K.: Investigating the Role of Selective Attention in Implicit Learning Using Overlapping Letter Strings. In: 28th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada (2006)
Vokey, J.R., Brooks, L.R.: Salience of Item Knowledge in Learning Artificial Grammars. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 18, 328–344 (1992)
Whittlesea, B.W., Wright, R.L.: Implicit (and explicit) learning: acting adaptively without knowing the consequences. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. 23, 181–200 (1997)
Winkielman, P., Schwarz, N., Fazendeiro, T., Reber, R.: The Hedonic Marking of Processing Fluency: Implications for Evaluative Judgement. The psychology of Evaluation: Affective Processes in Cognition and Emotion, 189–117 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhou, H., Wan, L., Fu, X. (2007). Generalized “Stigma”: Evidence for Devaluation-by-Inhibition Hypothesis from Implicit Learning. In: Paiva, A.C.R., Prada, R., Picard, R.W. (eds) Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction. ACII 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4738. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74889-2_60
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74889-2_60
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-74888-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-74889-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)