Abstract
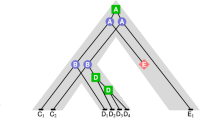
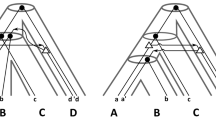
We consider two questions related to the evolution of gene families. First, given a gene tree for a gene family, can the evolutionary history of this family be explained with only speciation and duplication events, and without gene loss. We show that this question can be answered in linear time, and that such a gene tree induces a single species tree consistent with a history with no loss. We then present a heuristic for the following problem: if a gene tree can not be explained without gene loss, what is the minimum number of losses involved in an evolutionary history of the gene family. We finally evaluate our algorithms on a dataset of plants gene families.
Work supported by grants from NSERC and SFU.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvestad, L., Berglung, A.-C., Lagergren, J., Sennblad, B.: Gene tree reconstruction and orthology analysis based on an integrated model for duplications and sequence evolution. In: RECOMB 2004, pp. 326–335 (2004)
Blin, G., Chauve, C., Fertin, G., Rizzi, R., Vialette, S.: Comparing genomes with duplications: a computational complexity point of view. IEEE/ACM Trans. on Comput. Biol. and Bioinformatics (to appear, 2007)
Chen, K., Durand, D., Farach-Colton, M.: NOTUNG: a program for dating gene duplications and optimizing gene family trees. J. Comput. Biol. 7(3-4), 429–444 (2000)
Cotton, J.A., Page, R.D.M.: Going nuclear: gene family evolution and vertebrate phylogeny reconcilied. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 269, 1555–1561 (2002)
Durand, D., Haldórsson, B.V., Vernot, D.: A hybrid micro-macroevolutionary approach to gene tree reconstruction. J. Comput. Biol. 13(2), 320–3354 (2006)
Eichler, E.E., Sankoff, D.: Structural dynamics of eukaryotic chromosome evolution. Science 301(5634), 793–797 (2003)
Eulenstein, O., Mirkin, B., Vingron, M.: Comparison of annotating duplication, tree mapping, and copying as methods to compare gene trees with species trees. Mathematical hierarchies and biology, DIMACS Ser. Discrete Math. Theoret. Comput. Sci., Amer. Math. Soc., 37, 71–93 (1997)
Fares, M.A., Byrne, K.P., Wolfe, K.H.: Rate asymmetry after genome duplication causes substantial long-branch attraction artifacts in the phylogeny of Saccharomyces species. Mol. Biol. Evol. 23(2), 245–253 (2006)
Gorecki, P., Tiutyn, J.: DLS-trees: a model of evolutionary scenarios. Theoretical Comput. Sci. 359(1–3), 378–399 (2006)
Guigó, R., Muchnik, I., Smith, T.F.: Reconstruction of ancient phylogenies. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 6(2), 189–213 (1996)
Hallett, M.T., Lagergren, J.: New algorithms for the duplication-loss model. RECOMB 2000 , 138–146 (1996)
Lynch, M., Conery, J.S.: The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science 290(5494), 1151–1155 (2000)
Ma, B., Li, M., Zhang, L.: From gene trees to species trees. SIAM J. Comput. 30(3), 729–752 (2000)
Sanderson, M.J., McMahon, M.M.: Inferring angiosperm phylogeny from EST data with widespread gene duplication. BMC Evol. Biol. 7(Suppl. 1), S3 (2007)
Zmasek, C.M., Eddy, S.R.: A simple algorithm to infer gene duplication and speciation events on a gene tree. Bioinformatics 17(9), 821–828 (2001)
Zhang, L.: On a Mirkin-Muchnik-Smith conjecture for comparing molecular phylogenies. J. Comput. Biol. 4(2), 177–187 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chauve, C., Doyon, JP., El-Mabrouk, N. (2007). Inferring a Duplication, Speciation and Loss History from a Gene Tree (Extended Abstract). In: Tesler, G., Durand, D. (eds) Comparative Genomics. RECOMB-CG 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 4751. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74960-8_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74960-8_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-74959-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-74960-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)