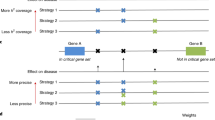
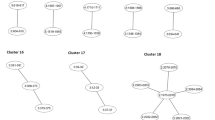
Comprehensive evaluation of common genetic variations through association of SNP structure with common complex disease in the genome-wide scale is currently a hot area in human genome research. Computational science, which includes computational intelligence, has recently become the third method of scientific enquiry besides theory and experimentation. Interest grew fast in developing and applying computational intelligence techniques to disease mapping using SNP and haplotype data. This review provides a coverage of recently developed theories and applications in computational intelligence for gene-gene and gene-environment interactions in complex diseases in genetic association study.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brookes AJ (1999) Review: The essence of SNPs. Gene (234) 177–186.
The International HapMap Consortium (2003) The International HapMap Project. Nature 426:789–796.
The International HapMap Consortium (2004) Integrating ethics and science in the International HapMap Project. Nat Rev Genet 5:467–475.
The International HapMap Consortium (2005) A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature, 437:1299–1320.
Daly MJ, Rioux JD, Schaffner SF, Hudson TJ, and Lander ES (2001) High-resolution haplotype structure in the human genome. Nat. Genet., 29, 229–232.
Cardon LR, Bell JI (2001) Association study designs for complex diseases. Nat Rev Genet 2:91–99.
Risch NJ (2000) Searching for genetic determinants in the new millennium. Nature 405:847–856.
Risch N, Merikangas K (1996) The future of genetics studies of complex human diseases. Science 273:1516–1517.
Stephens M and Donnelly P (2000) Inference in molecular population genetics. J R Stat Soc B 62:605–655.
Ioannidis JP, Gwinn M, Little J, Higgins JP, Bernstein JL, Boffetta P, Bondy M, Bray MS, Brenchley PE, Buffler PA, Casas JP, Chokkalingam A, Danesh J, Smith GD, Dolan S, Duncan R, Gruis NA, Hartge P, Hashibe M, Hunter DJ, Jarvelin MR, Malmer B, Maraganore DM, Newton-Bishop JA, O’Brien TR, Petersen G, Riboli E, Salanti G, Seminara D, Smeeth L, Taioli E, Timpson N, Uitterlinden AG, Vineis P, Wareham N, Winn DM, Zimmern R, and Khoury MJ (2006) Human Genome Epidemiology Network and the Network of Investigator Networks, A road map for efficient and reliable human genome epidemiology, Nature Genetics, 38(1):3–5.
Chatterjee N, Kalaylioglu Z, Moslehi R, Peters U, and Wacholder S (2006) Powerful multilocus tests of genetic association in the presence of gene-gene and gene-environment interactions. American Journal of Human Genetics, 79(6):1002–1016.
Cordell HJ, Barratt BJ, and Clayton DG (2004) Case/pseudocontrol analysis in genetic association studies: a unified framework for detection of genotype and haplotype associations, gene-gene and gene-environment interactions, and parent-of-origin effects. Genetic Epidemiology, 26(3):167–185.
Hunter DJ (2005) Gene-environment interactions in human diseases. Nature Reviews Genetics, 6:287–298.
Zondervan KT and Cardon LR (2004) The complex interplay among factors that influence allelic association. Nature Reviews Genetics, 5(2):89–100.
Azevedo L, Suriano G, van Asch B, Harding RM, and Amorim A (2006) Epistatic interactions: how strong in disease and evolution? Trends Genet.
Chapman, JM, Cooper JD, Todd JA, and Clayton DG (2003) Detecting disease associations due to linkage disequilibrium using haplotype tags: a class of tests and the determinants of statistical power. Hum. Hered. 56, 18–31.
Liu Z and Lin S (2005) Multilocus LD measure and tagging SNP selection with generalized mutual information. Genet Epidemiol. 29, 353–364.
Halldrsson BV, Bafna V, Lippert R, Schwartz R, De La Vega FM, Clark AG, and Istraili S (2004) Optimal Haplotype Block-Free Selection of Tagging SNPs for Genome-Wide Association Studies Genome Res. 14, 1633–1640.
Howie BN, Carlson CS, Rieder MJ, and Nickerson DA (2006) Efficient selection of tagging single-nucleotide polymorphisms in multiple populations. Human Genetics, 120(1):58–68.
Gopalakrishnan S and Qin ZS (2006) TagSNP Selection Based on Pairwise LD Criterion and Power Analysis in Association Studies. Pacific Sym. Biocomputing, 11:511–522.
Ke X. and Cardon LR (2003) Efficient selective screening of haplotypes tag SNPs. Bioinformatics, 19, 287–288.
Halperin E, Kimmel G, and Shamir R (2005) Tag SNP Selection in Genotype Data for Maximizing SNP Prediction Accuracy. Bioinformatics, 21(suppl 1): i195–i203, 2005.
Akey J, Jin L, and Xiong M (2001) Haplotypes vs single marker linkage disequilibrium tests: what do we gain? Eur J Hum Genet 9 (4), 291–300.
Zhu X, Zhang S, Kan D, and Cooper R (2004) Haplotype block definition and its application. Pacic Symposium on Biocomputing 9:152–163.
Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H, Moore JM, Roy J, Blumenstiel B, Higgins J, DeFelice M, Lochner A, Faggart M, Liu-Cordero SN, Rotimi C, Adeyemo A, Cooper R, Ward R, Lander ES, Daly MJ, and Altshuler D (2002) The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 296 (5576), 2225–2229.
Daly MJ, Rioux JD, Schaffner SF, Hudson TJ, Lander ES, Phillips MS, et al. (2003) Chromosome-wide distribution of haplotype blocks and the role of recombination hot spots. Nature Genet. 33, 382–387.
Zhang K, Calabrese P, Nordborg M, and Sun F (2002) Haplotype block structure and its applications to association studies: power and study designs. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 71, 1386–1394.
Meng Z, Zaykin DV, Xu CF, Wagner M, and Ehm MG (2004) Selection of genetic markers for association analyses, using linkage disequilibrium and haplotypes. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 73:115–130.
Anderson EC, and Novembre J (2003) Finding haplotype block boundaries by using the minimum-description-length principle. American Journal of Human Genetics, 73:336–354.
Mannila H, Koivisto M, Perola M, Varilo T, Hennah W, Ekelund J, Lukk M, Peltonen L, and Ukkonen E (2003) Minimum description length block finder, a method to identify haplotype blocks and to compare the strength of block boundaries. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 73, 86–94.
Zhang K, Deng M, Chen T, Waterman MS, and Sun F (2002) A dynamic programming algorithm for haplotype block partitioning. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 7335–7339.
Beckmann L, Thomas DC, Fischer C, and Chang-Claude J (2005) Haplotype sharing analysis using Mantel statistics, Human Heredity, 59:67–78.
Levin AM, Ghosh D, et al. (2005) A model-based scan statistics for identifying extreme chromosomal regions of gene expression in human tumors. Bioinformatics 21:2867–2874.
Schaid DJ, Rowland CM, Tines DE, Jacobson RM, and Poland GA (2002) Score test for association between traits and haplotypes when linkage phase is ambiguous. Am J Hum Genet 70:425–443.
Nothnagel M, Furst R, and Rohde K (2002) Entropy as a measure for linkage disequilibrium over multilocus haplotype blocks. Hum Hered, 54:186–198.
Hampe J, Schreiber S, and Krawczak M (2003) Entropy-based SNP selection for genetic association studies. Hum Genet. 114:36–43.
Zhao J, Boerwinkle E, and Xiong M (2005) An entropy-based statistic for genomewide association studies. American Journal of Human Genetics, 77:27–40.
Zaykin DV, Zhivotovsky LA, et al. (2002) Truncated product method for combining P-values. Genet Epidemio l22:170–185.
Ott J (2004) Issues in association analysis: error control in case-control association studies for disease gene discovery. Human Heredity, 58:171–174.
He J and Zelikovsky A (2006) MLR-tagging informative SNP selection for unphased genotypes based on multiple linear regression, Bioinformatics, 22(20):2558–2561.
Durrant C, Zondervan KT, Lon R, Cardon L, Hunt S, Deloukas P, and Morris AP (2004) Linkage Disequilibrium Mapping via Cladistic Analysis of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Haplotypes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 75, 35–43.
Baker SG (2005) A simple loglinear model for haplotype effects in a case-control study involving two unphased genotypes, Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology, 4(1):14.
Tzeng J, Wang C, Kao J, and Hsiao CK (2006) Regression-based association analysis with clustered haplotypes through use of genotypes. American Journal of Human Genetics, 78(2):231–242.
Burkett K, McNeney B, and Graham J (2004) A note on inference of trait associations with SNP haplotypes and other attributes in generalized linear models. Human Heredity, 57:200–206.
Greenspan G and Geiger D (2004) Model-based inference of haplotype block variation. J. Comp. Biol. 11, 493–504.
Greenspan G and Geiger D (2006) Modeling Haplotype Block Variation Using Markov Chains, Genetics, 172(4): 2583–2599.
Thomas DC, Stram DO, Conti D, Molitor J, and Marjoram P (2003) Bayesian spatial modeling of haplotype associations, Human Heredity, 56:32–40.
Schwender H and Ickstadt K (2006) Identification of SNP Interactions Using Logic Regression. http://www.sfb475.uni-dortmund.de/berichte/tr31-06.pdf (preprint)
Verzilli CJ, Stallard N, and Whittaker JC (2006) Bayesian graphical models for genomewide association studies. American Journal of Human Genetics, 79(1):100–112.
Ott J (2001) Neural networks and disease association studies. American Journal of Medical Genetics, Volume 105, Issue 1, 60–61.
Clark TG, De Iorio M, Griffiths RC, and Farrall M (2005) Finding associations in dense genetic maps: a genetic algorithm approach. Human Heredity, 60:97–108.
Lam JC, Roeder K, and Devlin B (2000) Haplotype fine mapping by evolutionary trees. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66 (2), 659–673.
Chang C, Huang Y, and Chao K (2006) A greedier approach for finding tag SNPs, Bioinformatics, 22(6):685–691.
Li J and Jiang T (2005) Haplotype-based linkage disequilibrium mapping via direct data mining, Bioinformatics, 21:4384–4393.
Lin Z and Altman RB (2004) Finding haplotype tagging SNPs by use of principal components analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 75: 850–861.
Horne BD and Camp NJ (2004) Principal component analysis for selection of optimal SNP-sets that capture intragenic genetic variation. Genetic Epidemiology, 26(1):11–21.
Ao S, Yip K, Ng M, Cheung D, Fong PY, Melhado I, and Sham PC (2005) CLUSTAG: hierarchical clustering and graph methods for selecting tag SNPs. Bioinformatics, 21(8):1735–1736.
Kooperberg C, Ruczinski I, LeBlanc M, and Hsu L (2001) Sequence Analysis Using Logic Regression. Genetic Epidemiology, 21:626–631.
Moore JH (2004) Genome-wide analysis of epistasis using multifactor dimensionality reduction: feature selection and construction in the domain of human genetics. In: Zhu, D. (eds.) Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining: Challenges and Realities with Real World Data, IGI.
Liu JS, Sabatti C, Teng J, Keats BJ, and Risch N (2001) Bayesian analysis of haplotypes for linkage disequilibrium mapping. Genome Research 11 (10), 1716–1724.
Molitor J, Marjoram P, and Thomas D (2003) Fine-Scale Mapping of Disease Genes with Multiple Mutations via Spatial Clustering Techniques. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73, 1368–1384.
Toivonen HT, Onkamo P, Vasko K, Ollikainen V, Sevon P, Mannila H, Herr M, and Kere J (2000) Data mining applied to linkage disequilibrium mapping. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67 (1), 133–145.
Ritchie MD, White BC, Parker JS, Hahn LW, and Moore JH (2003) PMID Optimization of neural network architecture using genetic programming improves detection and modeling of gene-gene interactions in studies of human diseases. BMC Bioinformatics 4:28.
Banzhaf W, Beslon G, Christensen S, Foster JA, Kepes F, Lefort V, Miller JF, Radman M, and Ramsden JJ (2006) Guidelines: From artificial evolution to computational evolution: a research agenda. Nat Rev Genet. Sep;7(9):729–35.
Moore JH and White BC (2006a) Exploiting expert knowledge for genome-wide genetic analysis using genetic programming. In: Runarsson et al. (eds.) Parallel Problem Solving from Nature - PPSN IX, Lecture Notes in Computer Science 4193, 969–977.
Foster JA. (2001) Evolutionary computation. Nat Rev Genet. 2(6):428–36.
Motsinger AA, Lee SL, Mellick G, and Ritchie MD (2006) GPNN: Power studies and applications of a neural network method for detecting gene-gene interactions in studies of human disease. BMC Bioinformatics. 25;7(1):39.
Motsinger AA, Fanelli TJ, and Ritchie MD (2006) Power of Grammatical Evolution Neural Networks to Detect Gene-Gene Interactions in the Presence of Error Common to Genetic Epidemiological Studies. International Genetic Epidemiology Society 15th Annual Meeting.
Pedrycz W (1997) Computational Intelligence: An Introduction. Boca Raton, FL, CRC
(2000) Pedrycz W and Vasilakos A (2000) Computational Intelligence in Telecommunications Networks. Boca Raton, FL, CRC.
Turing AM (1956) Can a machine think? In: Newman, J.R. (Ed.), The World of Mathematics, vol. 4. Simon and Schuster, New York, 2122.
Vasilakos A and Pedrycz W (2006) Ambient Intelligence, Wireless Networking, Ubiquitous Computing. ArtecHouse, MA, USA.
Fogel GB and Corne DW (2002) Evolutionary Computation in Bioinformatics. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco.
Moore JH and White BC (2006b) Detecting Epistatic Needles in Genome-Wide Haystacks. American human genetics conferences.
Hubley RM, Zitzler E, Roach JC (2003) Evolutionary algorithms for the selection of single nucleotide polymorphisms. BMC Bioinformatics 4:30.
Moore JH and Hahn LW (2002) A cellular automata approach to detecting interactions among single-nucleotide polymorphisms in complex multifactorial diseases. Pac Symp Biocomput. 53–64.
Onkamo P and Toivonen H (2006) A survey of data mining methods for linkage disequilibrium mapping. Human Genomics, Vol 2(1), 336–340(5).
Salem, RM, Wessel J, and Schork, NJ (2005) A comprehensive literature review of haplotyping software and methods for use with unrelated individuals. Human Genomics, Vol 2(1) pp. 39–66(28).
Molitor J, Marjoram P, Conti D, and Thomas D (2004) A survey of current Bayesian gene mapping methods. Human Genomics, Vol 1(5) pp. 371–374(4).
Shah SC and Kusiak A (2004) Data mining and genetic algorithm based gene/SNP selection. Artif Intell Med. (3):183–96.
McKinney BA, Reif DM, Ritchie MD, and Moore JH (2006) Machine Learning for Detecting Gene-Gene Interactions: A Review. Applied Bioinformatics. 5(2):77–88.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kelemen, A., Liang, Y., Vasilakos, A. (2008). Review of Computational Intelligence for Gene-Gene and Gene-Environment Interactions in Disease Mapping. In: Kelemen, A., Abraham, A., Liang, Y. (eds) Computational Intelligence in Medical Informatics. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 85. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75767-2_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75767-2_1
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-75766-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-75767-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)