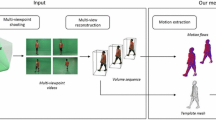
Abstract
This paper proposes a novel volume-based motion capture method using a bottom-up analysis of volume data and an example topology database of the human body. By using a two-step graph matching algorithm with many example topological graphs corresponding to postures that a human body can take, the proposed method does not require any initial parameters or iterative convergence processes, and it can solve the changing topology problem of the human body. First, three-dimensional curved lines (skeleton) are extracted from the captured volume data using the thinning process. The skeleton is then converted into an attributed graph. By using a graph matching algorithm with a large amount of example data, we can identify the body parts from each curved line in the skeleton. The proposed method is evaluated using several video sequences of a single person and multiple people, and we can confirm the validity of our approach.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gavrila, D.M.: The visual analysis of human movement: A survey. CVIU 73(1), 82–98 (1999)
Moeslund, T.B., Granum, E.: A survey of computer vision-based human motion capture. CVIU 81(3), 231–268 (2001)
Mikić, I., Trivedi, M., Hunter, E., Cosman, P.: Human body model acquisition and tracking using voxel data. International Journal of Computer Vision 53(3), 199–223 (2003)
Caillette, F., Howard, T.: Real-Time Markerless Human Body Tracking with Multi-View 3-D Voxel Reconstruction. In: Proc. of British Machine Vision Conference, vol. 2, pp. 597–606 (2004)
Kehl, M.B.R., Gool, L.V.: Full body tracking from multiple views using stochastic sampling. In: Proc. of CVPR 2005, vol. 2, pp. 129–136 (2005)
Cheung, G., Baker, S., Kanade, T.: Shape-from-silhouette of articulated objects and its use for human body kinematics estimation and motion capture. In: Proc. of CVPR 2003, vol. 1, pp. 77–84 (2003)
Chu, C.W., Jenkins, O.C., Matarić, M.J.: Markerless kinematic model and motion capture from volume sequences. Proc. of CVPR 2003 2, 475–482 (2003)
Sundaresan, A., Chellappa, R.: Segmentation and probabilistic registration of articulated body models. In: Proc. of ICPR 2006, vol. 2, pp. 92–96 (2006)
Laurentini, A.: The visual hull concept for silhouette-based image understanding. IEEE Trans. on PAMI 16(2), 150–162 (1994)
Saitoh, T., Mori, K., Toriwaki, J.: A sequential thinning algorithm for three dimensional digital pictures using the euclidean distance transformation and its properties. The transactions of the Institute of Electronics, Information and Communication Engineers. D-II J79-D-II (10), 1675–1685 (1996)
Brostow, G.J., Essa, I., Steedly, D., Kwatra, V.: Novel skeletal representation for articulated creatures. In: Pajdla, T., Matas, J. (eds.) ECCV 2004. LNCS, vol. 3023, pp. 66–78. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Messmer, B.T., Bunke, H.: A new algorithm for error-tolerant subgraph isomorphism detection. IEEE Trans. on PAMI 20, 493–504 (1998)
Quinlan, R.J.: Programs for Machine Learning. Morgan kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tanaka, H., Nakazawa, A., Takemura, H. (2007). Human Pose Estimation from Volume Data and Topological Graph Database. In: Yagi, Y., Kang, S.B., Kweon, I.S., Zha, H. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2007. ACCV 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4843. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-76386-4_58
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-76386-4_58
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-76385-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-76386-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)