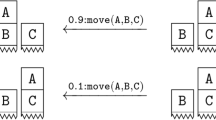
Abstract
Relational reinforcement learning is the application of reinforcement learning to structured state descriptions. Model-based methods learn a policy based on a known model that comprises a description of the actions and their effects as well as the reward function. If the model is initially unknown, one might learn the model first and then apply the model-based method (indirect reinforcement learning). In this paper, we propose a method for model-learning that is based on a combination of several SVMs using graph kernels. Indeterministic processes can be dealt with by combining the kernel approach with a clustering technique. We demonstrate the validity of the approach by a range of experiments on various Blocksworld scenarios.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. MIT Press, Cambridge (1998)
Bertsekas, D.P., Tsitsiklis, J.N.: Neuro-Dynamic Programming. Athena Scientific (1996)
Dzeroski, S., Raedt, L.D., Driessens, K.: Relational reinforcement learning. Machine Learning 43(1-2), 7–52 (2001)
Driessens, K., Ramon, J., Gärtner, T.: Graph kernels and gaussian processes for relational reinforcement learning. Machine Learning 64(1-3), 91–119 (2006)
Tadepalli, P., Givan, R., Driessen, K.: Relational reinforcement learning: An overview. In: Proceedings of the ICML 2004 Workshop on Relational Reinforcement Learning (2004)
van Otterlo, M.: A survey of reinforcement learning in relational domains. Technical report, CTIT Technical Report, TR-CTIT-05-31, July 2005, p. 70, CTIT Technical Report Series, ISSN 1381-3625 (2005)
Vapnik, V.N.: The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York (1995)
Kersting, K., Otterlo, M.V., Raedt, L.D.: Bellman goes relational. In: Brodley, C.E. (ed.) ICML, ACM, New York (2004)
Scanner, S., Boutilier, C.: Approximate linear programming for first-order mdps. In: Proceedings UAI 2005 (2005)
Hoelldobler, S., Karabaev, E., Skvortsova, O.: FluCaP: a heuristic search planner for first-order mdps. JAIR 27, 419–439 (2006)
Gärtner, T.: A survey of kernels for structured data. SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 5(1), 49–58 (2003)
Russell, S.J., Norvig, P.: Artificial intelligence: a modern approach. Prentice-Hall, USA (1995)
Gupta, N., Nau, D.S.: Complexity results for blocks-world planning. In: AAAI 1991. Proceedings of the Ninth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 2, pp. 629–633. AAAI Press/MIT Press, Anaheim, California, USA (1991)
Croonenborghs, T., Ramon, J., Blockeel, H., Bruynooghe, M.: Online learning and exploiting relational models in reinforcement learning. In: Veloso, M.M. (ed.) IJCAI, pp. 726–731 (2007)
Pasula, H., Zettlemoyer, L.S., Kaelbling, L.P.: Learning probabilistic relational planning rules. In: ICAPS, pp. 73–82 (2004)
Benson, S.: Inductive learning of reactive action models. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 47–54 (1995)
Wang, X.: Learning planning operators by observation and practice. In: Artificial Intelligence Planning Systems, pp. 335–340 (1994)
Gil, Y.: Learning by experimentation: Incremental refinement of incomplete planning domains. In: ICML, pp. 87–95 (1994)
Vere, S.A.: Inductive learning of relational productions. In: Waterman, D., Hayes-Roth, F. (eds.) Pattern-Directed Inference Systems, Academic Press, London (1978)
Geibel, P., Wysotzki, F.: Learning relational concepts with decision trees. In: Saitta, L. (ed.) Machine Learning: Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference, pp. 166–174. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (1996)
Chang, C.C., Lin, C.J.: LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines (2001), Software available at http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Halbritter, F., Geibel, P. (2007). Learning Models of Relational MDPs Using Graph Kernels. In: Gelbukh, A., Kuri Morales, Á.F. (eds) MICAI 2007: Advances in Artificial Intelligence. MICAI 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 4827. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-76631-5_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-76631-5_39
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-76630-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-76631-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)