Abstract
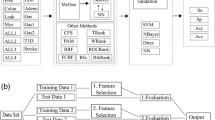
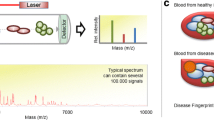
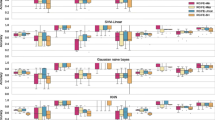
This paper proposes a novel feature selection technique for SELDI-TOF spectrum data. The new technique, called RISC (Relevance Index by Sample Counting) , measures the relevance of features based on each sample’s discriminating power to partition the samples in the opposite class. We also proposes a heuristic searching method to obtain the optimal feature set, which makes use of the relevance parameters. Our technique is fast even for extremely high-dimensional datasets such as SELDI spectrum, since it has low computational complexity and consists of simple counting operations. The new technique also shows good performance comparable to the conventional feature selection techniques from the experiment on three clinical datasets from NCI/CCR and FDA/CBER Clinical Proteomics Program Databank: Ovarian 4-3-02, Ovarian 7-8-02, Prostate.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petricoin, E.F., Ardekani, A.M., Hitt, B.A., Levine, P.J., Fusaro, V.A., Steinberg, S.M., et al.: Use of proteomic patterns in serum to identify ovarian cancer. Lancet 359(9306), 572–577 (2002)
Baggerly, K.A., Morris, J.S., Coombes, K.R.: Reproducibility of SELDI-TOF protein patterns in serum: comparing datasets from different experiments. Bioinformatics 20(5), 777–785 (2004)
Jong, K., Marchiori, E., Sebag, M., van der Vaart, A.: Feature Selection in Proteomic Pattern Data with Support Vector Machines. In: CIBCB, pp. 41–48. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2004)
Levner, I.: Feature selection and nearest centroid classification for protein mass spectrometry. BMC Bioinformatics (2005)
Lilien, R.H., Farid, H., Donald, B.R.: Probabilistic disease classification of expression-dependent proteomic data from mass spectrometry of human serum. Computational Biology (2003)
Tibshirani, R., Hastiey, T., Narasimhanz, T., Soltys, S., Shi, G., Koong, A., Le, Q.: Sample classifcation from protein mass spectrometry by peak probability contrasts. BioInformatics (2004)
Wu, B., Abbott, T., Fishman, D., McMurray, W., Mor, G., Stone, K., Ward, D., Williams, K., Zhao, H.: Comparison of statistical methods for classifcation of ovarian cancer using mass spectrometry data. BioInformatics 19(13) (2003)
Qu, Y., Adam, B., Yasui, Y., Ward, M.D., Cazares, L.H., Schellhammer, P.F., Feng, Z., Semmes, O.J., Wright, G.L.: Boosted decision tree analysis of surface-enhanced laser desortion/ionization mass spectral serum profiles discriminates prostate cancer from noncancer patients. Clinical Chemistry 48(10), 1835–1843 (2002)
Guyon, I., Elissee, A.: An introduction to variable and feature selection. Machine Learning, Special Issue on variable and feature selection 3, 1157–1182 (2003)
Kononenko, I.: Estimating attributes: Analysis and extensions of relief. In: ECML, pp. 171–182 (1994)
Biesiada, J., Duch, W.: Feature Selection for High-Dimensional Data: A Kolmogorov-Smirnov Correlation-Based Filter Solution. Computer Recognition Systems. In: Kurzynski, M., Puchała, E., Wozniak, M., Zolnierek, A. (eds.) CORES 2005. Proc. of the 4th International Conference on Computer Recognition Systems. Advances in Soft Computing, pp. 95–104. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Plant, C., Osl, M., Tilg, B., Baumgartner, C.: Feature Selection on High Throughput SELDI-TOF Mass-Spectrometry Data for Identifying Biomarker Candidates in Ovarian and Prostate Cancer. In: Proceedings of the Sixth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining – Workshops, pp. 174–179 (2006)
Marchiori, E., Jimenez, C.R., West-Nielsen, M., Heegaard, N.H.H.: Robust SVM-Based Biomarker Selection with Noisy Mass Spectrometric Proteomic Data. In: EvoWorkshops, pp. 79–90 (2006)
Peterson, L.E., Hoogeveen, R.C., Pownall, H.J., Morrisett, J.D.: Classification Analysis of Surface-enhanced Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectral Serum Profiles for Prostate Cancer. In: IJCNN 2006. International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 3828–3835 (2006)
Cormen, T.H., Leiserson, C.E., Rivest, R.L., Stein, C.: Introduction to Algorithms, Second Edition, Ch. 7, MIT Press and McGraw-Hill, Quicksort, pp. 145–164 (2001)
Cristianini, N., Shawe-Taylor, J.: Support Vector machines. Cambridge Press, Cambridge (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vu, TN., Ohn, SY., Kim, CW. (2007). RISC: A New Filter Approach for Feature Selection from Proteomic Data. In: Zhang, D. (eds) Medical Biometrics. ICMB 2008. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4901. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-77413-6_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-77413-6_3
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-77410-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-77413-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)