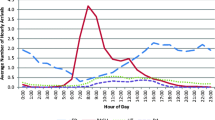
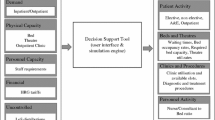
Summary
Multi-phase models of patient flow offer a practical but scientifically robust approach to the studying and understanding of the different streams of patients cared for by health care units. In this chapter, we put forward a decision support system that is specifically designed to identify the different streams of patient flow and to investigate the effects of the interaction between them by using readily available administrative data. The richness of the data dictate the use of data warehousing and On-Line Analytical Processing (OLAP) for data analysis and pre-processing; the complex and stochastic nature of health care systems suggested the use of discrete event simulation as the decision model. We demonstrate the application of the decision support system by reporting on a case study based on data of patients over 65 with a stroke related illness discharged by English hospitals over a year.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shaping the Future NHS: Long Term Planning for Hospitals and Related Services. (2000) Department of Health, London
Vasilakis C, Marshall AH (2005) Modelling nationwide hospital length of stay: opening the black box. J Oper Res Soc 56: 862–869
Millard PH (1994) Current measures and their defects. In: Millard PH, McClean SI (eds.) Modelling hospital resource use: a different approach to the planning and control of health care systems. Royal Society of Medicine, London, pp. 29–37
Smith PC, Goddard M (2002) Performance management and operational research: a marriage made in heaven? J Oper Res Soc 53: 247–255
Marshall AH, Vasilakis C, El-Darzi E (2005) Length of stay-based patient flow models: recent developments and future directions. Healthc Manag Sci 8: 213–220
McClean SI, Millard PH (1993) Patterns of length of stay after admission in geriatric medicine: an event history approach. The Statistician 42: 263–274
Harrison GW, Millard PH (1991) Balancing acute and long term care: the mathematics of throughput in departments of geriatric medicine. Methods Inf Med 30: 221–228
Wyatt S (1995) The occupancy management and planning system (BOMPS). The Lancet 345: 243–244
El-Darzi E, Vasilakis C, Chaussalet T, Millard PH (1998) A simulation modelling approach to evaluating length of stay, occupancy, emptiness and bed blocking in a hospital geriatric department. Healthc Manag Sci 1: 143–149
Marshall AH, McClean SI (2003) Conditional phase-type distributions for modelling patient length of stay in hospital. International Transactions in Operational Research 10: 565–576
Winter Report 2000–2001. (2001) Department of Health, London
Vasilakis C, El-Darzi E (2001) A simulation study of the winter bed crisis. Healthc Manag Sci 4: 31–36
Koutsoukis N-S, Mitra G, Lucas C (1999) Adapting on-line analytical processing for decision modelling: the interaction of information and decision technologies. Decis Support Syst 26: 1–30
Isken M, Littig SJ, West M (2001) A data mart for operations analysis. J Healthc Inf Manag 15: 143–153
Koutsoukis NS, Dominguez-Ballesteros B, Lucas C, Mitra G (2000) A prototype decision support system for strategic planning under uncertainty. Int J Phys Distrib Logistics Manag 30: 640–660
Phillips RL (1994) The Management Information Value Chain. Perspectives Issue 3: Available from www.stern.nyu.edu/~abernste/teaching/Spring2001/MIVC.htm, as of May 2007
Pedersen TB, Jensen CS (2001) Multidimensional Database Technology. Computer 34: 40–46
Codd EF, Codd SB, Salley CT (1993) Providing OLAP to User-Analysts: An IT Mandate. E.F. Codd & Associates, Sunnyvale, California
Vassiliadis P, Sellis T (1999) A survey of logical models for OLAP databases. ACM SIGMOD Rec 28: 64–69
Lee C, Vasilakis C, Kearney D, Pearse R, Millard PH (1998) The impact of the admission and discharge of stroke patients aged 65 and over on bed occupancy in English hospitals. Healthcare Manag Sci 1: 151–157
Gubitz G, Sandercock P (2000) Extracts from “Clinical Evidence”: Acute ischaemic stroke. Br Med J 320: 692–696
International classification of diseases, ninth revision (ICD-9). World Health Organisation, Geneva (1977)
Thomas H, Datta A (2001) A conceptual model and algebra for on-line analytical processing in decision support databases. Inf Syst Res 12: 83–102
Vasilakis C (2003) Simulating the flow of patients: an OLAP-enabled decision support framework. Ph.D. thesis, University of Westminster
Vasilakis C, El-Darzi E, Chountas P (2006) An OLAP-Enabled Environment for Modelling Patient Flow. Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS’06). pp. 261–266
Vasilakis C, El-Darzi E, Chountas P (2004) A Data Warehouse Environment for Storing and Analyzing Simulation Output Data. In: Ingalls RG, Rossetti MD, Smith JS, Peters BA (eds.) Proceedings of the 2004 Winter Simulation Conference. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Piscataway, New Jersey, pp. 703–710
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Vasilakis, C., El-Darzi, E., Chountas, P. (2008). A Decision Support System for Measuring and Modelling the Multi-Phase Nature of Patient Flow in Hospitals. In: Chountas, P., Petrounias, I., Kacprzyk, J. (eds) Intelligent Techniques and Tools for Novel System Architectures. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 109. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-77623-9_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-77623-9_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-77621-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-77623-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)