Abstract
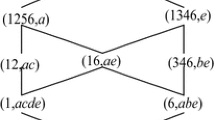
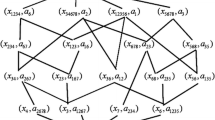
The theory of concept lattices is an efficient tool for knowledge discovery. To make the knowledge discovery of a larger formal context easier, this paper discusses the combination and decomposition of formal contexts when the attribute set is the same, and obtains the corresponding concept lattices. First, the methods how to obtain the whole concept lattice from sub-contexts of a larger formal context is proposed. Then, the converse situation is also studied, and the method how to obtain a sub-lattice from the original formal context is given. At the same time, the relationship between intension set of original context and that of its sub-context is analyzed. Finally, the combination and decomposition theories are generalized when there are multiple sub-contexts.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boucher-Ryan, P., Bridge, D.: Collaborative Recommending using Formal Concept Analysis. Knowledge-Based Systems 19(5), 309–315 (2006)
Carpineto, C., Romano, G.G.: An order-theoretic approach to conceptual clustering. In: Utgoff, P. (ed.) Proceedings of ICML 293, pp. 33–40. Elsevier, Amherst (1993)
Deogun, J.S., Saquer, J.: Concept approximations for formal concept analysis. In: Stumme, G. (ed.) Working with Conceptual Structures. Contributions to ICCS 2000, pp. 73–83. Verlag Shaker Aachen (2000)
Düntsch, I., Gediga, G.: Algebraic aspects of attribute dependencies in information systems. Fundamenta Informaticae 29(1-2), 119–133 (1997)
Ganter, B., Stumme, G., Wille, R.: Formal Concept Analysis, Foundations and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Ganter, B., Wille, R.: Formal Concept Analysis, Mathematical Foundations. Springer, Berlin (1999)
Godin, R.: Incremental concept formation algorithm based on Galois (concept) lattices. Computational Intelligence 11(2), 246–267 (1995)
Grigoriev, P.A., Yevtushenko, S.A.: Elements of an Agile Discovery Environment. In: Grieser, G., Tanaka, Y., Yamamoto, A. (eds.) DS 2003. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2843, pp. 309–316. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Ho, T.B.: An approach to concept formation based on formal concept analysis. IEICE Trans. Information and Systems E782D(5), 553–559 (1995)
Oosthuizen, G.D.: The Application of Concept Lattice to Machine Learning. Technical Report, University of Pretoria, South Africa (1996)
Oosthuizen, G.D.: Rough sets and concept lattices. In: Ziarko, W.P. (ed.) Rough Sets, and Fuzzy Sets and Knowledge Discovery (RSKD 1993), pp. 24–31. Springer, Heidelberg (1994)
Pagliani, P.: From concept lattices to approximation spaces: Algebraic structures of some spaces of partial objects. Fundamenta Informaticae 18(1), 1–25 (1993)
Wei, L.: Reduction theory and approach to rough set and concept lattice, PhD Thesis, Xi’an Jiaotong University. Xi’an Jiaotong University Press, Xi’an (2005)
Wille, R.: Restructuring lattice theory: an approach based on hierarchies of concepts. In: Rival, I. (ed.) Ordered sets, pp. 445–470. Reidel, Dordrecht-Boston (1982)
Wu, W.Z.: Attribute Granules in Formal Contexts. In: An, A., Stefanowski, J., Ramanna, S., Butz, C.J., Pedrycz, W., Wang, G. (eds.) RSFDGrC 2007. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4482, pp. 395–402. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Yao, Y.Y.: Concept lattices in rough set theory. In: Dick, S., Kurgan, L., Pedrycz, W., Reformat, M. (eds.) Proceedings of 2004 Annual Meeting of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society (NAFIPS 2004), IEEE Catalog Number: 04TH8736, June 27-30, pp. 796–801 (2004)
Zhang, W.X., Wei, L., Qi, J.J.: Attribute Reduction in Concept Lattice Based on Discernibility Matrix. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Rough Sets, Fuzzy Sets, Data Mining, and Granular Computing, Regina, Canada, August 31-September 3, pp. 157–165 (2005)
Zhao, Y., Yao, Y.Y.: Classification based on logical concept analysis. In: Proceedings of 19th Conference on the Canadian Society for Computational Studies of Intelligence (Canadian AI 2006), Québec City, Québec, Canada, June 7-9, pp. 419–430 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wei, L., Qi, JJ. (2008). Combination and Decomposition Theories of Formal Contexts Based on Same Attribute Set. In: Wang, G., Li, T., Grzymala-Busse, J.W., Miao, D., Skowron, A., Yao, Y. (eds) Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology. RSKT 2008. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 5009. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-79721-0_62
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-79721-0_62
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-79720-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-79721-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)