Abstract
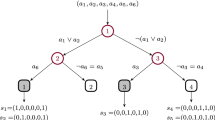
We give a (ln n + 1)-approximation for the decision tree (DT) problem. An instance of DT is a set of m binary tests T = (T 1, ..., T m ) and a set of n items X = (X 1, ..., X n ). The goal is to output a binary tree where each internal node is a test, each leaf is an item and the total external path length of the tree is minimized. Total external path length is the sum of the depths of all the leaves in the tree. DT has a long history in computer science with applications ranging from medical diagnosis to experiment design. It also generalizes the problem of finding optimal average-case search strategies in partially ordered sets which includes several alphabetic tree problems. Our work decreases the previous upper bound on the approximation ratio by a constant factor. We provide a new analysis of the greedy algorithm that uses a simple accounting scheme to spread the cost of a tree among pairs of items split at a particular node. We conclude by showing that our upper bound also holds for the DT problem with weighted tests.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alekhnovich, M., Braverman, M., Feldman, V., Klivans, A.R., Pitassi, T.: Learnability and automatizability. In: Proceedings of the 45th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 621–630. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos (2004)
Arkin, E.M., Meijer, H., Mitchell, J.S.B., Rappaport, D., Skiena, S.: Decision trees for geometric models. International Journal of Computational Geometry and Applications 8(3), 343–364 (1998)
Carmo, R., Donadelli, J., Kohayakawa, Y., Laber, E.S.: Searching in random partially ordered sets. Theor. Comput. Sci. 321(1), 41–57 (2004)
Chakaravarthy, V.T., Pandit, V., Roy, S., Awasthi, P., Mohania, M.K.: Decision trees for entity identification: approximation algorithms and hardness results. In: Libkin, L. (ed.) Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth ACM Symposium on Principles of Database Systems, pp. 53–62 (2007)
Feige, U., Lovász, L., Tetali, P.: Approximating min-sum set cover. Algorithmica 40(4), 219–234 (2004)
Garey, M.R.: Optimal binary identification procedures. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics 23(2), 173–186 (1972)
Garey, M.R., Graham, R.L.: Performance bounds on the splitting algorithm for binary testing. Acta Inf. 3, 347–355 (1974)
Garey, M.R., Johnson, D.S.: Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness. W.H. Freeman, New York (1979)
Hancock, T., Jiang, T., Li, M., Tromp, J.: Lower bounds on learning decision lists and trees. Information and Computation 126(2), 114–122 (1996)
Heeringa, B.: Improving Access to Organized Information. PhD thesis. University of Massachusetts, Amherst (2006)
Hyafil, L., Rivest, R.: Constructing optimal binary decision trees is np-complete. Information Processing Letters 5(1), 15–17 (1976)
Rao Kosaraju, S., Przytycka, T.M., Borgstrom, R.S.: On an optimal split tree problem. In: Dehne, F.K.H.A., Gupta, A., Sack, J.-R., Tamassia, R. (eds.) WADS 1999. LNCS, vol. 1663, pp. 157–168. Springer, Heidelberg (1999)
Laber, E.S., Nogueira, L.T.: On the hardness of the minimum height decision tree problem. Discrete Applied Mathematics 144(1-2), 209–212 (2004)
Moret, B.M.E.: Decision trees and diagrams. ACM Comput. Surv. 14(4), 593–623 (1982)
Moshkov, M.J.: Greedy algorithm of decision tree construction for real data tables. In: Transactions on Rough Sets, pp. 161–168 (2004)
Munagala, K., Babu, S., Motwani, R., Widom, J.: The pipelined set cover problem. In: ICDT, pp. 83–98 (2005)
Murthy, K.V.S.: On growing better decision trees from data. PhD thesis, The Johns Hopkins University (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Adler, M., Heeringa, B. (2008). Approximating Optimal Binary Decision Trees. In: Goel, A., Jansen, K., Rolim, J.D.P., Rubinfeld, R. (eds) Approximation, Randomization and Combinatorial Optimization. Algorithms and Techniques. APPROX RANDOM 2008 2008. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5171. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-85363-3_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-85363-3_1
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-85362-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-85363-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)