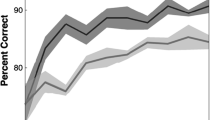
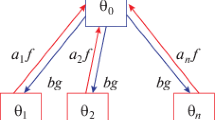
Abstract
We examine the dynamics of object recognition in a multi-layer network of oscillatory elements. The derivation of network dynamics is based on principles of sparse representation, and results in system behavior that achieves binding through phase synchronization. We examine the behavior of the network during recognition of objects with missing contours. We observe that certain network units respond to missing contours with reduced amplitude and temporal delay, similar to neuroscientific findings. Furthermore, these units maintain synchronization with a high-level object representation only in the presence of feedback.
Our results suggest that the illusory contour phenomena are formal consequences of a system that dynamically solves the binding problem, and highlight the functional relevance of feedback connections.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, D.: The time dimension for scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 16(6), 1401–1426 (2005)
Rao, A.R., Cecchi, G.A., Peck, C.C., Kozloski, J.R.: Unsupervised segmentation with dynamical units. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks (January 2008)
Rao, A.R., Cecchi, G.A., Peck, C.C., Kozloski, J.R.: Efficient segmentation in multi-layer oscillatory networks. In: IJCNN (accepted, 2008)
Lee, T.S., Mumford, D.: Hierarchical bayesian inference in the visual cortex. J. Optical Soc. America A 20(7), 1434–1448 (2003)
Grossberg, S., Mingolla, E.: Neural dynamics of perceptual grouping: textures, boundaries and emergent segmentations. Perception and Psychophysics 38, 141–171
Engel, A., Pascal, F., Singer, W.: Dynamic predictions: oscillations and synchrony in top-down processing. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2, 704–716 (2001)
Bar, M., et al.: Top-down facilitation of visual recognition. PNAS 103(2), 449–454 (2006)
Li, Z.: A neural model of contour integration in the primary visual cortex. Neural Compuation 10, 903–940 (1998)
Fukushima, K., Miyake, S., Ito, T.: Neocognitron: a neural network model for a mechanism of visual pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Systems, Man, and Cybernetics 13(3), 826–834 (1983)
Galuske, R., et al.: The role of feedback representations in cat visual cortex. PNAS 99(26), 17083–17088 (2002)
Lamme, V., Roelfsema, P.: The distinct modes of vision offered by feedforward and recurrent processing. Trends in Neuroscience 23, 571–579 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rao, A.R., Cecchi, G. (2008). Spatio-temporal Dynamics during Perceptual Processing in an Oscillatory Neural Network. In: Kůrková, V., Neruda, R., Koutník, J. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks - ICANN 2008. ICANN 2008. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5164. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-87559-8_71
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-87559-8_71
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-87558-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-87559-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)