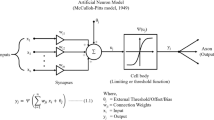
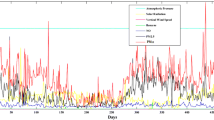
Abstract
The understanding and management of air quality problems is a suitable problem concerning the application of artificial intelligence (AI) methods towards knowledge discovery for the purposes of modelling and forecasting. As air quality has a direct impact on the quality of life and on the general environment, the ability to extract knowledge concerning relationships between parameters that influence environmental policy making and pollution abatement measures becoming more and more important. In the present paper an arsenal of AI methods consisting of Neural Networks and Principal Component Analysis is being supported by a set of mathematical tools including statistical analysis, fast Fourier transformations and periodograms, for the investigation and forecasting of photochemical pollutants time series in Athens, Greece. Results verify the ability of the methods to analyze and model this knowledge domain and to forecast the levels of key parameters that provide direct input to the environmental decision making process.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slini, T., Karatzas, K., Papadopoulos, A.: Regression analysis and urban air quality forecasting: An application for the city of Athens. Global Nest: the Int. J. 4, 153–162 (2002)
Gallant, S.I.: Perceptron-based learning algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 1(2), 179–191 (1990)
Kohonen, T.: Self-Organizing Maps, Series in Information Sciences, 2nd edn.1997, vol. 30. Springer, Heidelberg (1995)
Hornik, K., Stinchcombe, M., White, H.: Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Networks 2, 359–366 (1989)
Lippman, R.P.: An introduction to computing with neural nets. IEEE ASSP Magazine (1987)
Slini, T., Karatzas, K., Mousiopoulos, N.: Correlation of air pollution and meteorological data using neural networks. Int. J. Environment and Pollution 20(1-6), 218–229 (2004)
Chelani, A.B., Gajghate, D.G., Hasan, M.Z.: Prediction of ambient PM10 and toxic, metals using artificial neural networks. J. of Air and Waste Management Ass. 52, 805–810 (2002)
Comrie, A.C.: Comparing neural networks and regression models for ozone forecasting. J. of Air and Waste Management Ass. 47, 653–663 (1997)
Kolhmainen, M., Martikainen, H., Ruuskanen, J.: Neural networks and periodic components used in air quality forecasting. In: Atmospheric Environment, vol. 35, pp. 815–825 (2001)
Perez, P., Trier, A.: Prediction of NO and NO2 concentrations near a street with heavy traffic in Santiago, Chile. Atmospheric Environment 35(21), 1783–1789 (2001)
Bordignon, S., Gaetan, C., Lisi, F.: Nonlinear models for groundlevel ozone forecasting. Statistical Methods and Applications 11, 227–246 (2002)
Huang, L.S., Smith, R.L.: Meteorologically-dependent trends in urban ozone, National Institute of Statistical Sciences, Technical Report 72 (1997)
Kim, H.Y., Guldmann, J.M.: Modeling air quality in urban areas: A cell-based statistical approach. Geographical Analysis, 33 (2001)
Chen, L.-J., Islam, S., Biswas, P.: Nonlinear dynamics of hourly ozone concentrations: Nonparametric short term prediction. Atmospheric Environment 32, 1839–1848 (1998)
Shiva Nagendra, S.M., Khare, M.: Artificial neural network approach for modelling nitrogen dioxide dispersion from vehicular exhaust emissions. Ecological Modelling 190, 99–115 (2006)
Zolghadri, A., Monsion, M., Henry, D., Marchionini, C., Petrique, O.: Development of an operational model-based warning system for tropospheric ozone concentrations in Bordeaux, France. Environmental Modelling & Software 19, 369–382 (2004)
Kalapanidas, E., Avouris, N.: Short-term air quality prediction using a case-based classifier. Environmental Modelling & Software 16, 263–272 (2001)
Barrero, M.A., Grimalt, J.O., Canto´n, L.: Prediction of daily ozone concentration maxima in the urban atmosphere. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems 80, 67–76 (2006)
Briggsa, D.J., de Hoogh, C., Gulliver, J., Wills, J., Elliott, P., Kingham, S., Smallboned, K.: A regression-based method for mapping traffic-related air pollution: application and testing in four contrasting urban environments. The Science of the Total Environment 253, 151–167 (2000)
Athanasiadis, I.N., Karatzas, K.D., Mitkas, P.A.: Classification techniques for air quality forecasting. In: 17th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2006)
Kassomenos, P., Karakitsios, S., Papaloukas, C.: Estimation of daily traffic emissions in a South-European urban agglomeration during a workday. Evaluation of several “what if” scenarios. Science of The Total Environment 370, 480–490 (2006)
Ch. Chatzis, E., Alexopoulos, A.: Indoor and outdoor personal exposure to benzene in Athens, Greece. Science of The Total Environment 349, 72–80 (2005)
Roussos P.L.,Giannis T.: Applied statistics in the social sciences (Second revised publication), Ellhnika Grammata, Athens (2006)
Smith, L.I.: A tutorial on Principal Components Analysis (February 26, 2002)
Lance, C., Butts, M., Michels, L.: The sources of four commonly reported cutoff criteria: What did they really say? Organizational Research Methods 9, 202–220 (2006)
Garson, G.D.: Professor of Public Administration Editor, Social Science Computer Review College of Humanities and Social Sciences, http://www2.chass.ncsu.edu/garson/pa765/factor.htm
Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, “Fourier transform”, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourier_transform
StatSoft, Inc. © Copyright, 1984-2003, “Neural Networks”, http://www.statsoft.com/textbook/stneunet.html
Matlab Help. Keywords: Neural Network Toolbox
Saini, L.M., Soni, M.K.: Artificial neural network based peak load forecasting using Levenberg-Marquardt and quasi-Newton methods. Generation, Transmission and Distribution, IEE Proceedings 149(5), 578–584 (2002)
European Environment Agency and World Health Organisation, Air and Health - Local authorities, health and environment (1999), http://reports.eea.europa.eu/2599XXX/en/page008.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Karatzas, K.D., Papadourakis, G., Kyriakidis, I. (2009). Understanding and Forecasting Air Pollution with the Aid of Artificial Intelligence Methods in Athens, Greece. In: Koutsojannis, C., Sirmakessis, S. (eds) Tools and Applications with Artificial Intelligence. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 166. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88069-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88069-1_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-88068-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-88069-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)