Abstract
Web systems for air quality information and pollution modeling provide access to daily measured and predicted valuable information for the internet users. There are just a few examples around the world in this area. A recently developed web system at http://airpol.fatih.edu.tr is one such application. It provides information about air quality prediction for Istanbul, Turkey in a user friendly interface. New studies have been performed to increase the prediction efficiencies of the system and presented in this work.
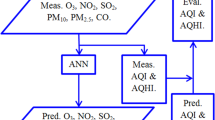
This paper presents a study on the prediction of carbon monoxide (CO) levels using Artificial Neural Networks (ANN). ANN models have been applied to the prediction of 3 day CO levels into future. The observed and predicted values were compared to determine the performance of the ANN models. The experimental results shows that spatial parameters (Universal Transverse Mercator coordinates) generally produce better forecasting (30% error) than ordinary, non-spatial parameters, although there are some cases where spatial parameters yield lower prediction accuracy. The experiments reveal that models with spatial input variables deserve further study and better models could be developed with higher accuracy.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurt A., Gulbagci B., Karaca F., Alagha O., (2008) An Online Air Pollution Forecasting System Using Neural Networks, Environ. Int. 34(5) 592-598.
Oktay A.B., (2006) “Air Pollution Forecasting By Using Data Mining”; MSc. Dissertation, Science and Engineering Institute, Fatih University, Istanbul, Turkey.
F. Karaca, O. Alagha, F. Ertürk, (2005) Application of inductive learning: Air pollution forecast in Istanbul City, Intel. Auto. Soft Comp., 11: 207-216.
Karaca, F.; Nikov, A.; Alagha, O. (2006) NN-AirPol: a neural-networks-based method for air pollution evaluation and control; Int. J. Environ. Pol., 28: 310-325.
N. Künzli, R. Kaiser, S. Medina, P. Filliger, (2001) Public health and air pollution, The Lancet , 357 (9249): 71.
Nikov A., F., Karaca, O. Alagha, A. Kurt, H. Hakkoymaz, (2005) AirPolTool: A web based tool for Istanbul air pollution forecasting and control, proceedings of 3rd International symposium on Air Quality Management at urban, regional and global, Istanbul, Turkey, September 26-30; Paper 118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kurt, A., Oktay, A.B., Karaca, F., Alagha, O. (2009). Artificial neural networks based modelling of carbon monoxide: Effects of spatial parameters. In: Athanasiadis, I.N., Rizzoli, A.E., Mitkas, P.A., Gómez, J.M. (eds) Information Technologies in Environmental Engineering. Environmental Science and Engineering(). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88351-7_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88351-7_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-88350-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-88351-7
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)