Abstract
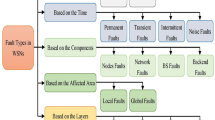
As the nodes have limited battery power in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), energy efficiency and fault tolerance should be the two major issues in designing WSNs. However, previous studies on positioning base stations (BSs) in WSNs are focused on energy efficiency only. Yet, mission-critical applications like emergency medical care systems should be guaranteed continuous services considering fault tolerance. In this paper we propose to place multiple BSs considering not only energy efficiency but also fault tolerance. We present two strategies to find the optimal position of BSs; (1) minimizing the average transmission energy for energy efficiency; and (2) minimizing additional energy consumption after a BS failure for fault tolerance. The optimal positions for multiple BSs are derived by the metric that considers both energy efficiency and fault tolerance, with a weight factor. Our simulation results show that fault tolerance is important and strongly related to elongation of network lifetime. In addition, we show that our proposed scheme is more energy-effective than previously suggested strategies on unexpected environmental changes which occur commonly in WSNs and sustain the network lifetime effectively under BS failures.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gandham, S.R., et al.: Energy efficient schemes for wireless sensor networks with multiple mobile base stations. In: Proc. IEEE GLOBECOM (2003)
Vaas, D., Vidacs, A.: Positioning mobile base station to prolong wireless sensor network lifetime. In: Proc. ACM CoNEXT (2005)
Zimmermann, K., et al.: Self-management of wireless base stations. In: Proc. IEEE MICMC (2005)
Ganesan, D., et al.: Highly resilient, energy efficient multipath routing in wireless sensor networks. In: Proc. ACM MobiHoc (2001)
Krishnamchari, B., et al.: The energy-robustness tradeoff for routing in wireless sensor networks. In: Proc. IEEE ICC (2003)
Sha, K., et al.: WEAR: A balanced, fault-tolerant, energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Sensor Networks 1(2) (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kim, S., Ko, J., Yoon, J., Lee, H. (2008). Energy-Efficient and Fault-Tolerant Positioning of Multiple Base Stations. In: Vazão, T., Freire, M.M., Chong, I. (eds) Information Networking. Towards Ubiquitous Networking and Services. ICOIN 2007. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5200. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-89524-4_58
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-89524-4_58
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-89523-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-89524-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)