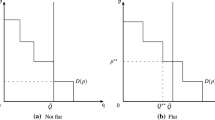
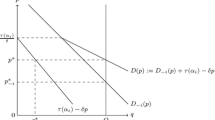
Abstract
To study the allocating problem of total permitted pollution discharge capacity(TPPDC), an allocation method with variable supply based on the uniform price auction of divisible goods is proposed in this paper firstly. Then, a linear equilibrium bidding strategy of this new method is given. Lastly, the incentive compatibility and validity of this method are proved. Therefore, this method will provide valuable theoretical basis and guidance for building the pollution emission permits trade system.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma, Z., Dudek, D.: Pollutant Gross Control and Pollutant Discharge Right Trade. Chinese Environment Science Publishing Company, Beijing (1999)
Ortega Reichert, A.: A Sequential Game with Information Flow. Chapter 8 in Models for Competitive Bidding under Uncertainty, Stanford University. PhD Thesis, 232–254 (1981)
Harris, M., Raviv, A.: A Theory of Monopoly Pricing Schemes with Demand Uncertainty. American Economic Review 71, 347–365 (1981)
Maskin, E., Riley, J.: Optimal Multi-Unit Auction. In: Fed, H. (ed.) The Economics of Missing Markets. Information and Games. Oxford University Press, New York (1989)
Back, K., Zender, J.F.: Auctions of Divisible Goods: on the Rationale for the Treasury Experiment. Review of Financial Studies 6, 733–764 (1993)
Back, K., Zender, J.F.: Auctions of Divisible Goods with Endogenous Supply. Economics Letters 73, 29–34 (2001)
Wang, J.J.D., Zender, J.F.: Auctioning Divisible Goods. Economic Theory 19, 673–705 (2002)
Kremer, I., Nyborg, K.: Divisible-Good Auctions: the Role of Allocation Rules. Rand Journal of Economics 35, 147–159 (2004)
Damianov, D.S.: The Uniform Price Auction with Endogenous Supply. Economics Letters 77, 101–112 (2005)
Indranil, C., Richard, E.W.: Asymptotic Prices in Uniform-Price Multi-Unit Auctions. Economic Theory 4, 983–987 (2005)
Zhao, Y., Borthwick, A., Wang, Q.: Competition Allocation of Total Permitted Pollution Discharge Capacity Based on Divisible Goods Auction. European Journal of Operational Research (in press, 2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rao, C., Zhang, Z., Liu, J. (2009). Allocation Method of Total Permitted Pollution Discharge Capacity Based on Uniform Price Auction. In: Yu, W., He, H., Zhang, N. (eds) Advances in Neural Networks – ISNN 2009. ISNN 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5551. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01507-6_121
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01507-6_121
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-01506-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-01507-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)