Abstract
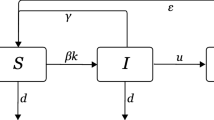
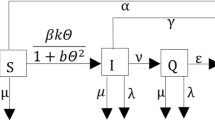
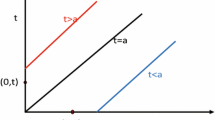
In this paper, we proposed a susceptible-infected model with variant infection rates because different individuals have different resistance to diseases in different periods of real epidemic events. We consider two cases: Case 1, we know every individual’s infection rate to a kind of epidemic, satisfy a type of distribution. Case 2, assume all individuals have same initial infection rates, a susceptible individual’s infection rate will be less than the initial rate if he is not infected after limited number of contacts with infected ones. For both two cases, at the time tD, preventive and control measures bring into effects, every individual’s infection rate would decrease. We implemented this models on scale-free networks, and found that the epidemic process before the time tD in Case 1 is almost the same as that in Standard SI model if the infection rate in Standard SI model equals the mean infection rate in Case 1. Furthermore, using numerical simulation, we analysis the effects of the parameter tD, and find the bimodal distribution of final infection rates. Finally, we conclude what we get in this paper and give our future direction.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pastor-Satorras, R., Vespignani, A.: Epidemics and Immunization in Scale-free Networks. In: Bornholdt, S., Schuster, H.G. (eds.) Handbook of Graph and Networks. Wiley-VCH, Berlin (2003)
Zhou, T., Fu, Z.Q., Wang, B.H.: Prog. Nat. Sci. 16, 452 (2006)
Pastor-Satorras, R., Vespignani, A.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 3200 (2001)
Pastor-Satorras, R., Vespignani, A.: Phys. Rev. E 63, 066117 (2001)
May, R.M., Lloyd, A.L.: Phys. Rev. E 64, 066112 (2001)
Moreno, Y., Pastor-Satorras, R., Vespignani, A.: Eur. Phys. J. B 26, 521 (2002)
Ke, H., Yi, T.: Temporal Behaviors of Epidemic Spreading on the Scale-free Network. Physica A 373, 845–850 (2007)
Zhou, et al.: Behaviors of Susceptible-infected Epidemics on Scale-free Networks with Identical Infectivity. Physical Review 74, 056109 (2006)
Barthélemy, M., Barrat, A., Pastor-Satorras, R., Vespignani, A.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 178701 (2004)
Barthélemy, M., Barrat, A., Pastor-Satorras, R., Vespignani, A.: J. Theor. Biol. 235, 275 (2005)
Zhou, T., Yan, G., Wang, B.H.: Phys. Rev. E 71, 046141 (2005)
Olinky, R., Stone, L.: Phys. Rev. E 70, 030902 (2004)
Fa, D.S., Zhai, F.Y., Ge, K.Y., Chen, F.N.: Distributions of Body Mass Index of Chinese Adults. Journal of Hygiene Research 6, 209–215 (2001)
Zhen, Z.K., Ma, L., Chen, H.Y.: The Study of the Distribution of the Chinese BMI. Mathematical Theory and Application 3, 312–315 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hong, L., Ouyang, M., Mao, Z., Chen, X. (2009). Epidemic Spreading with Variant Infection Rates on Scale-Free Network. In: Yu, W., He, H., Zhang, N. (eds) Advances in Neural Networks – ISNN 2009. ISNN 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5553. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01513-7_103
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01513-7_103
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-01512-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-01513-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)