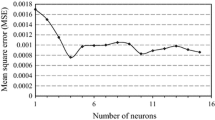
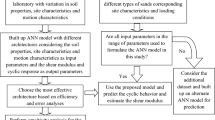
Abstract
In this chapter a neural network-based finite element method is presented for modeling of the behavior of soils under cyclic loading. The methodology is based on the integration of a neural network in a finite element framework. In this method, a neural network is trained using experimental (or in-situ) data representing the mechanical response of material to applied load. The trained network is then incorporated in the finite element analysis to predict the constitutive relationships for the material. The development and validation of the method will be presented followed by the application to study of the behavior of soils under cyclic loading. The results of the analyses will be compared with those obtained from standard finite element analyses using conventional constitutive models. The merits and advantages of neural network-based constitutive models and the intelligent finite element model will be highlighted. It will be shown that the neural network-based constitutive models offer an effective and unified approach to constitutive modeling of materials with complex behavior in finite element analysis of boundary value problems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shin, H.S., Pande, G.N.: On self-learning finite element codes based on response of structures. J. Computers and Geotechnics 27, 161–171 (2000)
Javadi, A.A., Tan, T.P., Zhang, M.: Neural network for constitutive modeling in finite element analysis. J. Computer Assisted Mechanics and Engineering Sciences 10, 523–529 (2003)
Javadi, A.A., Tan, T.P., Elkassas, A.S.I., Zhang, M.: An Intelligent Finite Element Method: Development of the Algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 6th World Congress on Computational Mechanics. Tsinghua University Press /Springer, Beijing (2004)
Javadi, A.A., Farmani, R., Tan, T.P.: An intelligent self-learning Genetic Algorithm; development and engineering applications. In: International Journal of Advanced Engineering Informatics (in print) (2005)
Pao, Y.H.: Adaptive pattern recognition and neural networks. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, USA (1989)
Hinton, E., Owen, D.R.J.: Finite element programming. Academic Press, London (1977)
Duncan, J.M., Chang, C.Y.: Nonlinear analysis of stress and strain in soils. ASCE Journal of Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division SM5, 1629–1653 (1970)
Ghaboussi, J., Garret, J.H., Wu, X.: Knowledge-based modeling of material behavior with neural networks. Journal of Engineering Mechanics Division (ASCE) 117, 32–153 (1991)
Ghaboussi, J., Sidarta, D.: A new nested adaptive neural network for modeling of constitutive behavior of materials. J. Computers and Geotechnics 22, 29–52 (1998)
Hashash, Y.M., Jung, S., Ghaboussi, J.: Numerical implementation of a neural network based material model in finite element analysis. Int. Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 5, 989–1005 (2004)
Lefik, M., Schrefler, B.: Artificial neural network as an incremental nonlinear constitutive model for a finite element code. J. Computational Methods in Applied Mechanical Engineering 192, 3265–3283 (2003)
Millar, D.L., Clarici, E., Calderbank, P.A., Marsden, J.R.: On the practical use of a neural network strategy for the modeling of the deformability behavior of Croslands Hill sandstone rock. In: Proceedings of the APCOM XXV Conference, Brisbane, pp. 457–465 (1995)
Moses, G.G., Rao, S.N., Rao, P.N.: Undrained strength behavior of a cemented marine clay under monotonic and cyclic loading. J. Ocean Engineering 30, 1765–1789 (2003)
Osinov, V.A.: Cyclic shearing and liquefaction of soil under irregular loading: an incremental model for the dynamic earthquake-induced deformation. J. Soil Dynamic and Earthquake Engineering 23, 535–548 (2003)
Rao, S.N., Panda, A.P.: Non-linear analysis of undrained cyclic strength of soft marine clay. J. Ocean Engineering 26(3), 241–253 (1998)
Usaborisut, P., Koike, M., Bahalayodhin, B., Niyamapa, T., Yoda, A.: Cyclic torsional shear loading test for an unsaturated, hollowed specimen using Bangkok clayey, soil. J. Terramechanics 38, 71–87 (2001)
Yilmaz, M.T., Pekcan, O., Bakir, B.S.: Undrained cyclic shear and deformation behavior os silt-clay mixture of Adapazari, Turkey. J. Soil Dynamic and Earthquake Engineering 24, 497–507 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Javadi, A.A., Tan, T.P., Elkassas, A.S.I. (2009). Intelligent Finite Element Method and Application to Simulation of Behavior of Soils under Cyclic Loading. In: Abraham, A., Hassanien, AE., Snášel, V. (eds) Foundations of Computational Intelligence Volume 5. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 205. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01536-6_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01536-6_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-01535-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-01536-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)