Abstract
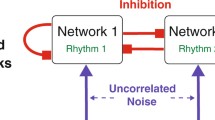
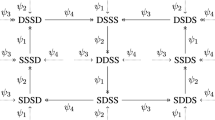
Fully-connected neural networks of non-linear half-center oscillators coupled both electrically and synaptically may exhibit a variety of modes of oscillation despite fixed topology and parameters. In suitable circumstances it is possible to switch between these modes in a controlled fashion. Previous work has investigated this phenomenon the simplest possible 2 cell network. In this paper we show that the 4 cell network, like the 2 cell, exhibits a variety of symmetrical and asymmetrical behaviours. In general, with increasing electrical coupling the number of possible behaviours is reduced until finally the only expressed behaviour becomes in-phase oscillation of all neurons. Our analysis enables us to predict general rules governing behaviour of more numerous networks, for instance types of co-existing activity patterns and a subspace of parameters where they emerge.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riehle, A., Grun, S., Diesmann, M., Aersten, A.: Spike synchronization and rate modulation differently involved in motor cortical functions. Science 278, 1950–1953 (1997)
McCormick, D.A., Contreras, D.: On the cellular and network basis of epileptic seizures. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 63, 815–846 (2001)
Traub, R.D., Jeffreys, J.G.R., Whittington, M.A.: Simulations of gamma rhythms in networks of interneurons and pyramidal cells. J. Comp. Neurosci. 4, 141–150 (1997)
Wang, X.J., Buzsaki, G.: Alternating and synchronous rhythms in reciprocally inhibitory model networks. Neural Comp. 4, 84–97 (1992)
Whittington, M.A., Traub, R.D., Jeffreys, J.G.R.: Synchronized oscillations in interneuron networks driven by metabotropic glutamate receptor activation. Nature 373, 612–615 (1995)
Terman, D., Bose, A., Kopell, N.: Functional reorganization in thalamocortical networks: Transitions between spindling and delta sleep rhythms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 15417–15422 (1996)
Rubin, J., Terman, D.: Geometric analysis of population rhythms in synaptically coupled neuronal networks. Neural Comp. 12, 597–645 (2000)
Galaretta, M., Hestrin, S.: A network of fast-spiking cells in the neocortex connected by electrical synapses. Nature 402, 72–75 (1999)
Gibson, J.R., Belerlein, M., Connors, B.W.: Two networks of electrically coupled inhibitory neurons in neocortex. Nature 402, 75–79 (1999)
Traub, R.D., Kopell, N., Bibbig, A., Buhl, E.H., Le Beau, F.E.N., Wittington, M.A.: Gap junctions between interneuron dendrites can enhance synchrony of gamma oscillations in distributed networks. J. Comp. Neurosci. 21, 9478–9486 (2001)
Lewis, T., Rinzel, J.: Dynamics of spiking neurons connected by both inhibitory and electrical coupling. J. Comp. Neurosci. 14, 283–309 (2003)
Bem, T., Rinzel, J.: Short duty cycle destabilizes half-center oscillator but gap junctions can restabilize the anti-phase pattern. J. Neurophysiol. 91, 693–703 (2004)
Lopez da Silva, F.H., Blanes, W., Kalitzin, S.N., Parra, J., Suffczynski, P., Velis, D.N.: Epilepesis as dynamic deaseas of brain systems: basic models of the transitions between normal and epileptic activity. Epilepsia 44, 72–83 (2003)
Bem, T., Le Feuvre, Y., Rinzel, J., Meyrand, P.: Electrical coupling induces bistability of rhythms in networks of inhibitory spiking neurons. European J. Neurosci. 22, 2661–2668 (2004)
Hallam, J., Ijspeert, A.J.: Using evolutionary methods to parameterize neural models: a study of the lamprey central pattern generator. In: Duro, R.J., Santos, J., Grana, M. (eds.) Biological Inspired Robot Behavior Engineering. Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing, vol. 109. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Mundon, T., Murray, A.F., Hallam, J., Patel, L.N.: Causal neural control of a latched ocean wave point absorber. In: Duch, W., Kacprzyk, J., Oja, E., Zadrożny, S. (eds.) ICANN 2005. LNCS, vol. 3697, pp. 423–429. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Merriam, E.B., Netoff, T.I., Banks, M.I.: Bistable Network behaviour of Layer-I Interneurons in Auditory Cortex. J. Neurosci. 25(26), 6175–6186 (2005)
Selverston, A.I., Moulin, M.: Oscillatory neural networks. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 47, 29–48 (1985)
Rowat, P., Selverston, A.I.: Modeling the gastric mill central pattern generator of the lobster with a relaxation-oscillator network. J. Neurophysiol. 70, 1030–1053 (1993)
Cohen, A.H., Rossignol, S., Grillner, S. (eds.): Neural control of rhythmic movements of vertebrates. Wiley, New York (1988)
Bem, T., Hallam, J., Meyrand, P., Rinzel, J.: Electrical coupling and bistability in inhibitory neural networks. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering 26, 3–14 (2006)
Goloub, D., Wang, X.J., Rinzel, J.: Synchronization properties of spindle oscillations in a thalamic reticular nucleus model. J. Neurophysiol. 72, 1109–1126 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bem, T., Hallam, J. (2009). Characterisation of Multiple Patterns of Activity in Networks of Relaxation Oscillators with Inhibitory and Electrical Coupling. In: Mira, J., Ferrández, J.M., Álvarez, J.R., de la Paz, F., Toledo, F.J. (eds) Methods and Models in Artificial and Natural Computation. A Homage to Professor Mira’s Scientific Legacy. IWINAC 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5601. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02264-7_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02264-7_18
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-02263-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-02264-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)